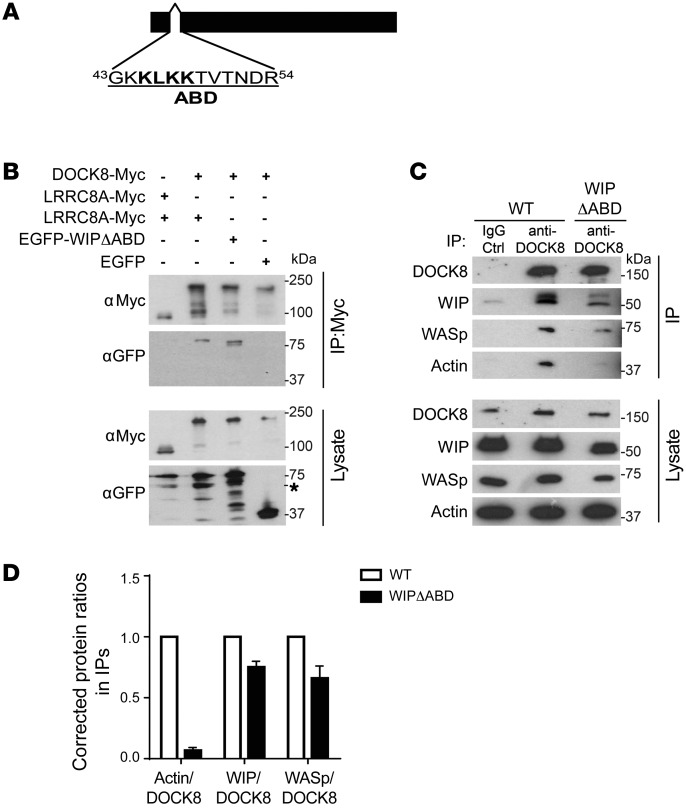
Figure 3. WIP bridges DOCK8 to actin.
(A) Map of the WIPΔABD protein. (B) Representative immunoblot of the co-IP of WIP-EGFP and WIPΔABD-EGFP with Myc-tagged DOCK8 in 293T cell transfectants. LRRC8A-Myc and EGFP transfectants were used as negative controls, and an aliquot of the lysates used for the coprecipitation was probed for Myc and EGFP to ensure equal loading. The * denotes a non-specific band. (C and D) Representative immunoblot (C) and quantitative analysis (D) of the co-IP of WIP, WASp, and actin with DOCK8 in splenic T cells from WT and WIPΔABD knockin mice. An aliquot of the lysates used for the co-IP was probed for DOCK8, WIP, WASp, and actin as a loading control. Quantification of the results was performed by calculating the relative ratio of actin/DOCK8, WIP/DOCK8, and WASp/DOCK8 in DOCK8 immunoprecipitates relative to lysates and normalizing the values to those obtained in WT T cells by setting the WT ratio to 1. Ctrl, control. Data are representative of 3 independent experiments in B and 2 independent experiments in C and D. Error bars in D represent the mean ± SEM.