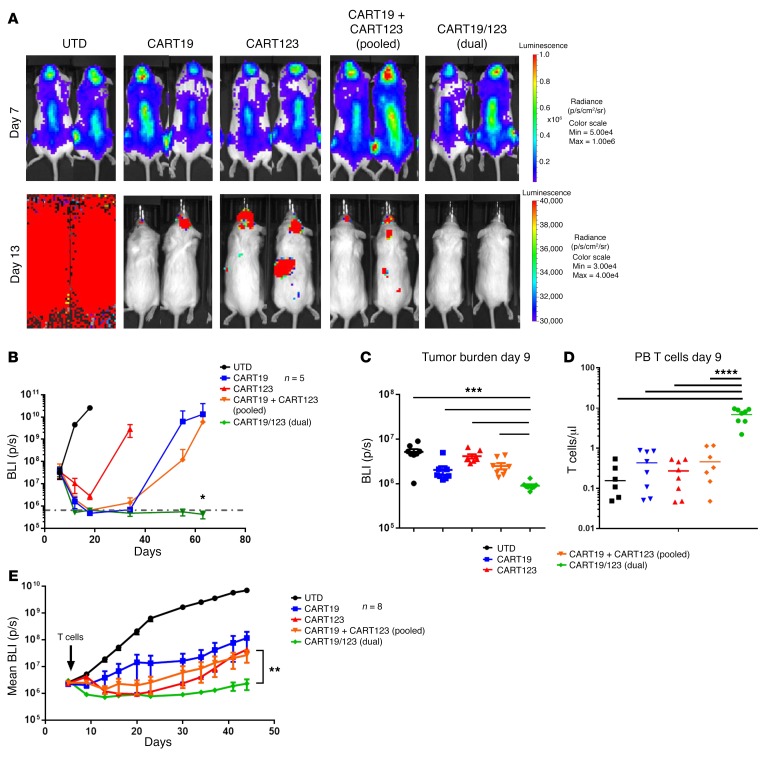
Figure 6. Dual CART19/123 cells are highly effective against B-ALL in vivo.
(A) NSG mice were engrafted with a B-ALL cell line (NALM6, CBG+). At day 7, mice were randomized based on tumor burden (BLI) to receive control T cells (UTD), CART19, CART123, the 1:1 pooled combination of CART123 and CART19, or the dual CART19/123 (same total number of CAR+ cells). The tumor burden 6 days after T cell infusion (day 13) is shown in the graph: the deepest short-term antileukemia response is observed in the dual CART group. Monitoring of tumor burden (BLI) over time shows that only the dual CART19/123-treated mice have long-term CR (P = 0.02 at day 63). (B) Bioluminescence imaging of mice receiving the different treatments at day 7 (before T cell infusion) and day 13 (6 days after T cell infusion). Only mice receiving dual CART19/123 reached a quick and deep complete response. All graphs representative of 2 independent experiments. (C) In a primary B-ALL xenograft model (patient UPN#11), dual CART19/123 have a superior antileukemia activity (shown as reduced bioluminescence) as compared with pooled CART19 + CART123 at early time point (day 9), and this was correlated by a significantly higher T cell engraftment in the PB (D). (E) Tumor burden imaging (as mean bioluminescence) demonstrated a better antileukemia activity of dual CART19/123 as compared with pooled CART19 + CART123 or single CART. Panels B–E are representative of at least 2 independent experiments. Student’s t test was used to compare 2 groups; in analysis where multiple groups were compared, 1-way ANOVA was performed with Holm-Šidák correction for multiple comparisons. When multiple groups at multiple time points/ratios were compared, the Student’s t test or ANOVA for each time point/ratio was used. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001.