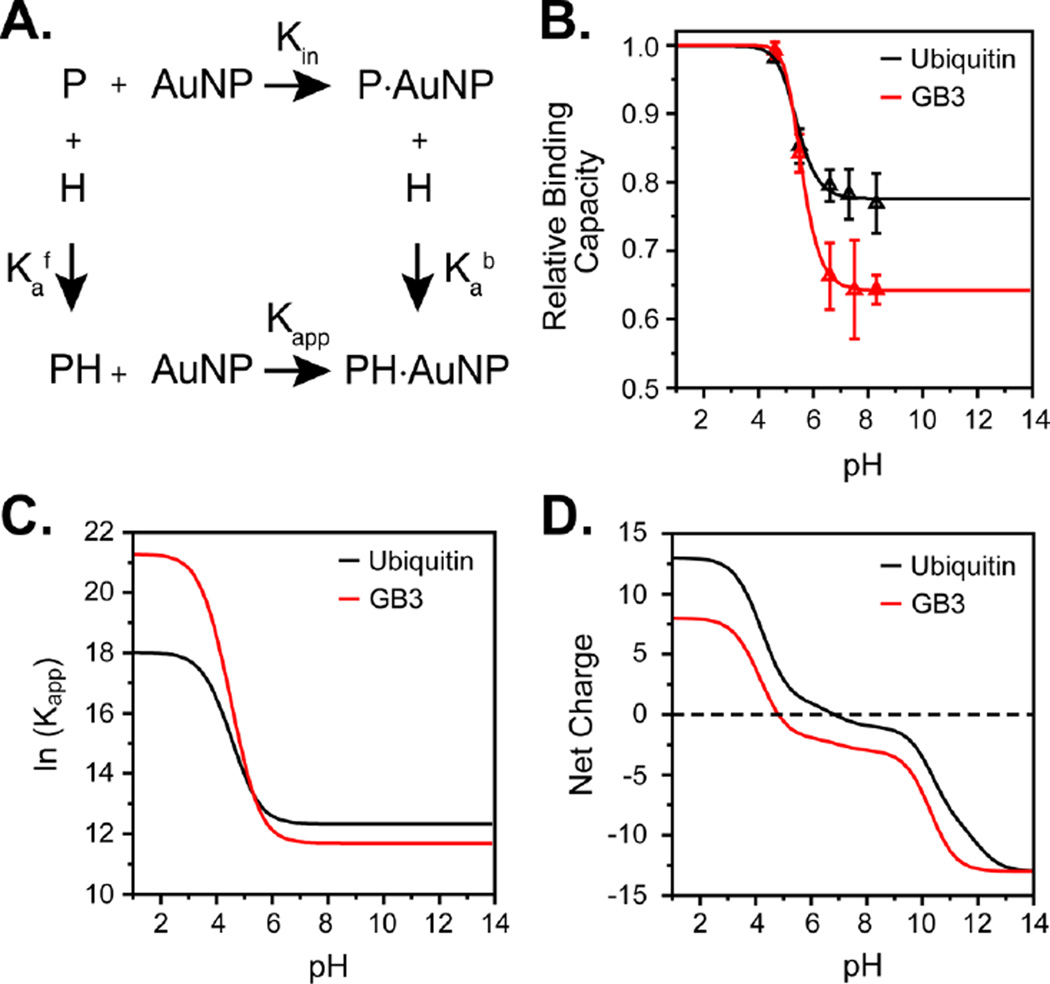
Figure 3.
pH-dependent model for protein–AuNP binding. (A) Thermodynamic cycle demonstrating binding for a single site. Kin and Kapp are the intrinsic and apparent association constants, respectively, relative to the reference state described in the text; and are the acid dissociation constants of protein in the free and bound states, respectively. The model used in the text uses multiple binding sites (described in the SI). (B) Measured pH-dependent binding capacities of GB3 (red) and ubiquitin (black) after model fitting. Triangles represent the average observed binding for three independent measurements, and solid lines represent the fitted model. (C) Apparent binding affinity (ln Kapp) vs pH for GB3 and ubiquitin, demonstrating an increase for GB3 at low pH. (D) Net charge per protein (Z) of the GB3 and ubiquitin molecules as a function of pH using model-compound pKa values.