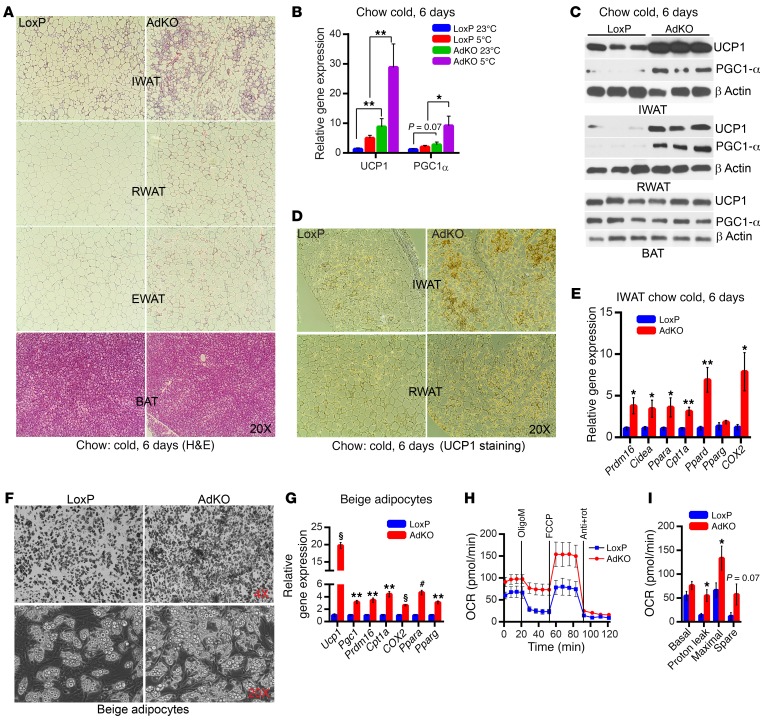
Figure 5. Adipocyte-specific Ip6k1 deletion enhances browning.
(A) Chronic cold enhances adipose tissue remodeling that resembles browning in CD-AdKOs (image represents data from 3 individual mice per group). (B) Ucp1 and Pgc1 expression levels are higher in AdKOs at 23°C and are further enhanced by chronic cold exposure (n = 6 mice per group; 1-way ANOVA). (C) Chronic cold enhances PGC1-α and UCP1 protein levels in CD-AdKO IWAT and RWAT (n = 3 mice per group). (D) Immunohistochemistry reveals enhanced UCP1 protein levels in chronic-cold-exposed CD-AdKO IWAT and RWAT (images represent results obtained from n = 3 mice per group). (E) Browning and thermogenic and mitochondrial EE machinery are upregulated in chronic-cold-exposed CD-AdKOs (n = 6 mice per group; t test). (F) SVFs (n = 6 mice per preparation) isolated from AdKO IWAT display enhanced beige adipogenesis. Images represent results obtained from at least 3 independent experiments. (G) Beige and mitochondrial activity markers are upregulated in AdKO IWAT beige adipocytes (n = 6 mice per preparation; triplicate samples). (H) OCR is higher in AdKO IWAT beige adipocytes (n = 6 mice per preparation; 10 replicates). OligoM, oligomycin; Anti, antimycin A; rot, rotenone. (I) Quantification of H reveals that average proton leak and maximal respiratory capacity are significantly higher in AdKO IWAT beige adipocytes. Data in all panels are expressed as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, #P < 0.001, §P < 0.0001.