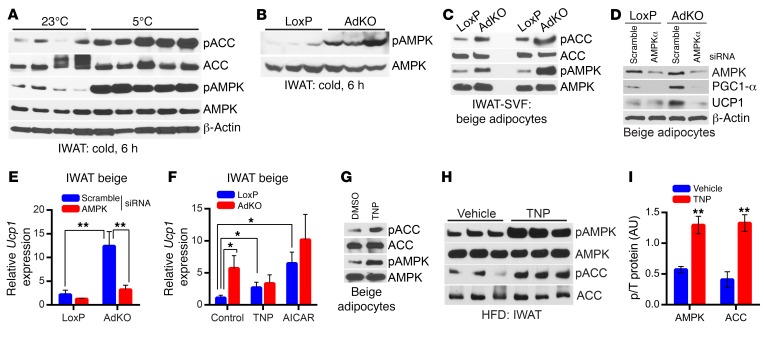
Figure 6. IP6K1 reduces AMPK-mediated adipocyte browning.
(A) AMPK stimulatory phosphorylation (T172) and its activity are enhanced in WT mice following acute cold exposure (n = 4–5 mice per group). (B) AMPK phosphorylation is dramatically augmented in acute-cold-exposed AdKOs (n = 3 mice per group). (C) AMPK activity is higher in 2 separate preparations (n = 6 mice per preparation) of AdKO beige adipocytes differentiated from IWAT SVF in vitro. (D) siRNA-mediated AMPKα depletion substantially reduces AMPKα protein level in LoxP and AdKO beige adipocytes. Moreover, PGC1-α and UCP1 protein levels, which are higher in AdKO adipocytes, are reduced following AMPKα depletion. Data represent results obtained from 2 independent experiments. (E) Ucp1 mRNA expression is slightly reduced by AMPKα siRNA treatment in LoxP mice. Conversely, Ucp1 expression, which is significantly higher in AdKO adipocytes compared with LoxPs, is substantially reduced following AMPKα depletion. Data represent results obtained from 5 experimental replicates. (F) AdKO beige adipocytes express higher levels of Ucp1 compared with LoxP adipocytes under basal conditions (control). TNP (5 μM, 16 hours) substantially enhances Ucp1 expression in LoxP adipocytes, whereas it does not influence Ucp1 in AdKO adipocytes. The AMPK activator AICAR enhances Ucp1 expression to a higher extent in LoxP adipocytes. Data represent results obtained from 5 experimental replicates. (G) TNP (5 μM) enhances AMPK phosphorylation and activity in beige adipocytes differentiated in vitro from isolated from WT IWAT SVF. Immunoblot represents results from at least 3 independent experiments. (H and I) A single dose of TNP (20 mg/kg body weight; i.p.) enhances AMPK phosphorylation and activity on ACC in the IWAT of HFD-fed mice (n = 3 mice per group; t test). Data in all panels are expressed as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.