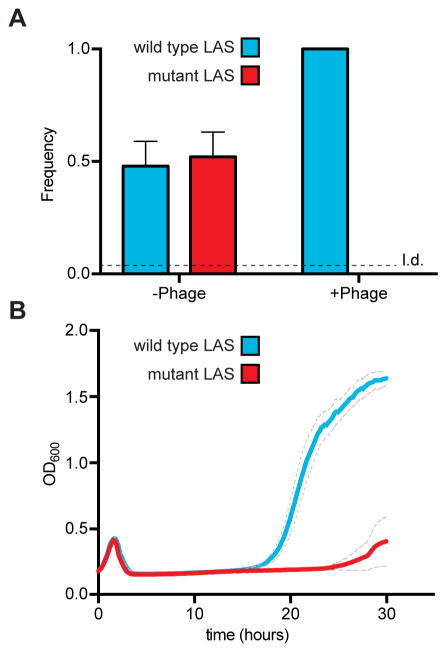
Figure 3. The LAS confers a fitness benefit during CRISPR-Cas immunity.
See also Fig. S2.
(A) Analysis of culture composition following direct competition between strains harboring the wild-type or mutant LAS. Strains were mixed in a 1:1 ratio and infected with phage ϕNM4γ4 at an MOI of 1. Once the infection completed, the cultures were streaked onto a plate and colonies were picked to determine their LAS by Sanger sequencing (n = 16 per condition per replicate, 96 colonies tested in total). Mean ± S.E.M. of three replicas are reported. L.d, limit of detection.
(B) Growth of cultures infected with phage ϕNM4γ4 followed by the measurement of optical density at 600 nm (OD600). Cell containing a wild-type or mutant LAS were infected and their OD600 was followed over time. While most cells die after infection, a small fraction can acquire new spacers and resume growth after viral clearance through CRISPR-Cas immunity. Mean ± S.E.M. (grey dotted line) of three replicas are reported.