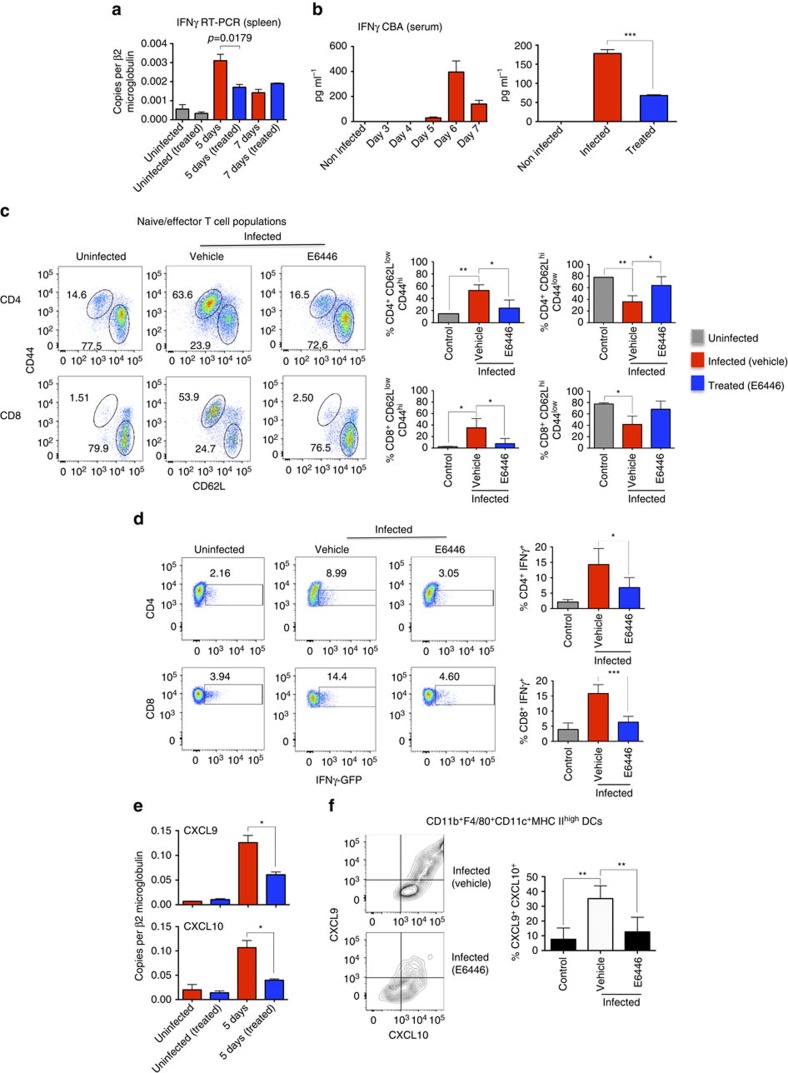
Figure 6. E6446 inhibits expression of IFNγ by T cells and CXCL9 and CXCL10 by MO-DCs.
C57BL/6, GREAT and REX3 mice were infected with PbA and treated with either E6446 (120 mg kg−1 per day) or vehicle from −1 to 3 days post infection. (a) Spleens were harvested from WT mice at 0, 5 and 7 post infection, total RNA extracted and expression levels of IFNγ mRNA analysed by quantitative PCR. The results were normalized to β2-MICROBULIN. (b) Sera from infected C57BL/6 mice were collected at different times post infection and used to measure the levels of IFNγ by Cytometric Bead Analysis. The inhibitory effect of E6446 on the levels of circulating IFNγ was evaluated at 6 days post infection (right panel). (c) Spleens from untreated and E6446-treated C57BL6 mice were harvested 5 days post infection. Cells were gated on CD44 and CD62L from CD4+ or CD8+. Bar graphs correspond to the percentage of naive (CD62LhighCD44low) versus activated effector (CD62LlowCD44 high) CD4+ T (top panels) and CD8+ T (bottom panels) cells. (d) Splenocytes from uninfected and infected GREAT mice treated with E6446 or left untreated were stimulated with PMA (50 ng ml−1) and ionomycin (500 ng ml−1) for 4 h in culture containing brefeldin A and analysed by flow cytometry gated on CD4+ or CD8+ cells. YFP-positive cells were considered as IFNγ producers CD4+ T (top panels) and CD8+ T (bottom panels) cells. (e) Quantitative reverse transcriptase–PCR (left panels) and (f) flow cytometry analysis revealed that treatment with E6446 resulted in inhibition of CXCL9 and CXCL10 mRNA expression in the spleen and RFP and BFP proteins by splenic MO-DCs from PbA-infected C57BL/6 and REX3 mice, respectively. Representative primary flow cytometry dot plots are shown in c–f. Results are representative of two to three independent experiments with three to five mice per group. Differences considered statistically significant when *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 or ****P<0.0001, as indicated by two-way analysis of variance analysis (values are means±s.d.).