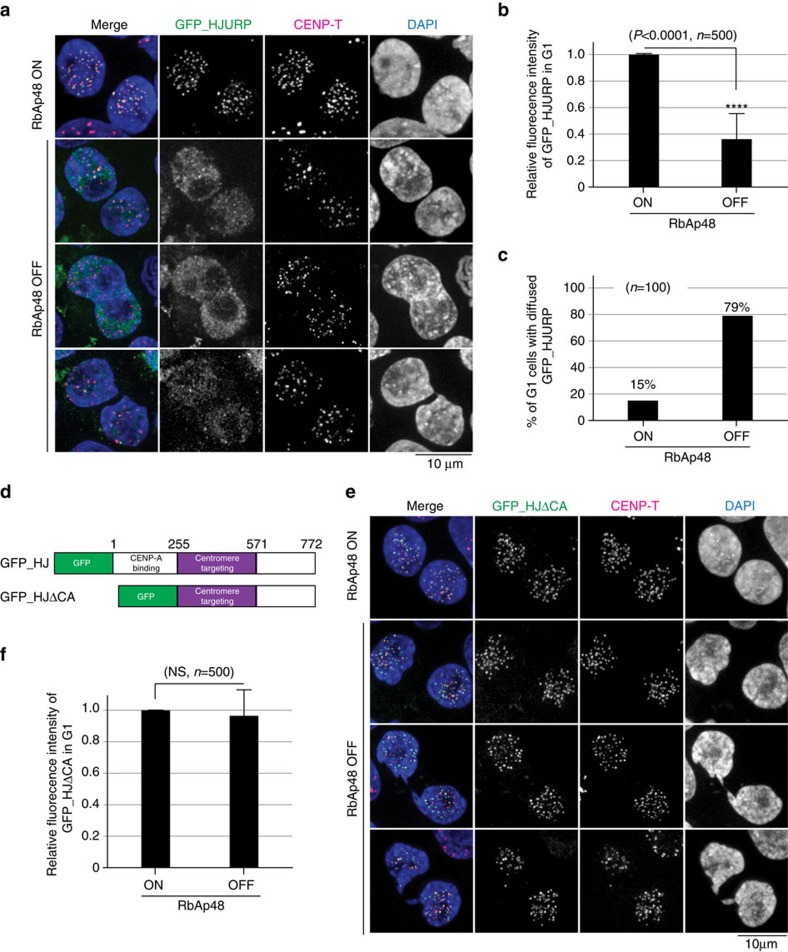
Figure 5. HJURP do not properly recognize centromeres in RbAp48-deficient cells.
(a) Localization of HJURP in RbAp48 ON or OFF cells stably expressing GFP-HJURP. CENP-T was used as a centromere marker. Bar, 10 μm. (b) Quantification of GFP-HJURP intensities at centromeres (shown in a) in RbAp48 ON or OFF G1 cells. Five hundred centromeres in 100 different G1 cells were quantified for each measurement. G1 cells were judged by cell size and daughter cell-like morphology. Error bars represent s.d. Asterisk indicates statistically significance (P<0.0001) by Student's t-test. (N=500). (c) Percentages of cells that displayed diffused GFP-HJURP in RbAp48 ON or OFF G1 cells expressing GFP-HJURP. Definition of diffused GFP-HJURP is in Supplementary Fig. 5E. (N=100). (d) Diagram of chicken HJURP protein. The N-terminal region (1–254 aa) is responsible for CENP-A binding. The middle region (255–571 aa) is essential for its centromere localization. We prepared GFP fused full-length HJURP (GFP_HJ) and HJURP lacking CENP-A binding region (GFP_HJΔCA). (e) Localization of N-terminal truncated HJURP (GFP_HJΔCA) in RbAp48 ON or OFF cells stably expressing GFP_HJΔCA. CENP-T was used as a centromere marker. Bar, 10 μm. (f) Quantification of GFP_HJΔCA intensities at centromeres in RbAp48 ON or OFF cells. Five hundred centromeres in 100 different cells were quantified for each measurement. Error bars represent s.d. of centromere intensity. Relative intensities are shown.