Figure 1.
Genome-wide Profiling of Allelic DNA Methylation
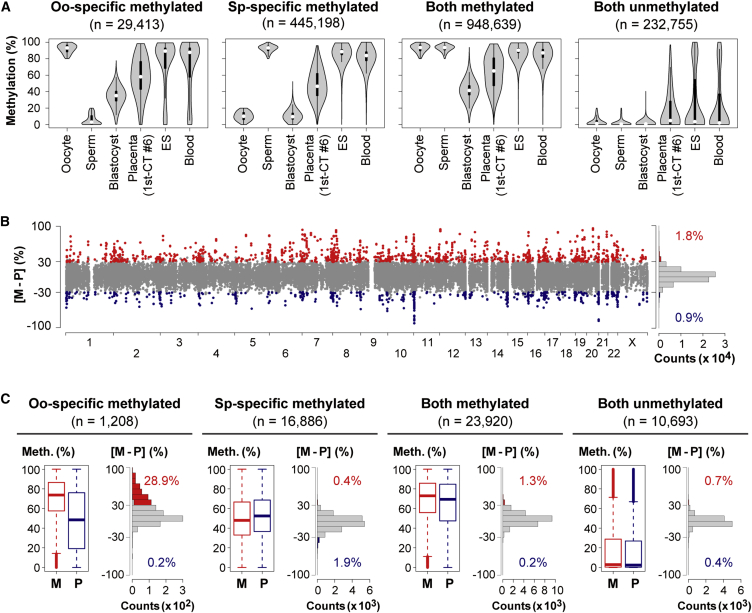
(A) Violin plots of methylation levels of windows hypermethylated (≥80%) or hypomethylated (≤20%) in one or both gametes (window size = 20 CpGs, step size = 10 CpGs). We compared the methylation profile of the CT cells (1st-CT #6 [♀]) with those of human gametes, blastocysts, cord blood cells (DRA003802),10 and ES cells (GSM706059).31 Oo-specific (Sp-specific) methylated windows are defined as windows hypermethylated in oocytes (sperm) and hypomethylated in sperm (oocytes). Thin and thick lines are boxplots, and white dots indicate the median.
(B) Chromosomal distribution of maternally and paternally methylated windows in 1st-CT #6. The x and y axes show chromosome numbers and the maternal methylation level minus the paternal methylation level ([M − P] level), respectively. Windows showing ≥30% [M − P] levels and statistically significant allelic methylation differences (BH-corrected p < 0.05) are shown in red, and those with ≤ −30% [M − P] levels are in blue. The other windows are in gray. A histogram of the distribution of the [M − P] levels and the proportions of maternally and paternally methylated windows are also shown.
(C) Boxplots of methylation levels of the maternal (M) and paternal (P) alleles of windows in 1st-CT #6. Boxes represent lower and upper quartiles, and horizontal lines indicate the median. Whiskers extend to the most extreme data points within 1.5 times the interquartile range from the boxes. The open circles indicate the data points outside the whiskers. Histograms of the distribution of the [M − P] levels are also shown (colored as defined in [B]).