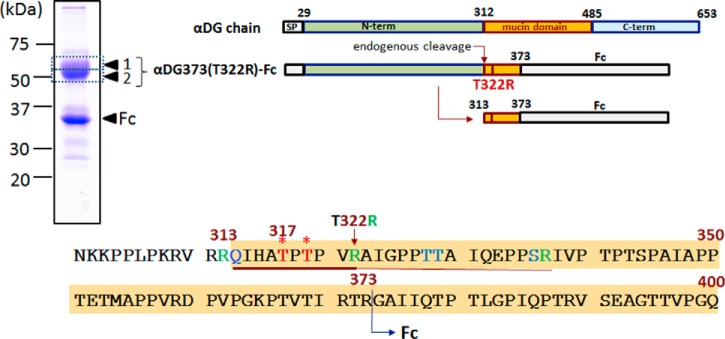
Fig. 1.
Recombinant αDG constructs and amino acid sequence of N301-Q400. The full-length αDG chain consists of an N-terminal domain (N-term) that is lost upon endogenous processing via furin-like cleavage (14), yielding a mature product starting at Q313. The inclusion of this domain in the recombinant αDG construct is, however, necessary as it is required for proper laminin-binding glycan formation at Thr317/Thr319 (5) (marked with asterisks). For the αDG373(T322R)-Fc product used in this study, an Fc domain is fused to R373, in place of the mucin-like and C-terminal domains. A tryptic cleavage site was introduced via T322R mutation, which allowed formation of a 10-amino acid tryptic peptide carrying only two threonine sites for O-glycosylation. The recombinant products, expressed and purified by protein G Sepharose from HEK293T cells, ran as two major bands on SDS-PAGE corresponding to ∼35 and 50–60 kDa. Only the upper band, excised, in-gel digested, and analyzed as bands 1 and 2 yielded similar tryptic peptides corresponding to the αDG mucin domain, whereas the lower band only gave peptides derived from the Fc domain. The entire amino acid sequence of αDG373(T322R)-Fc is shown in supplemental Fig. S1.