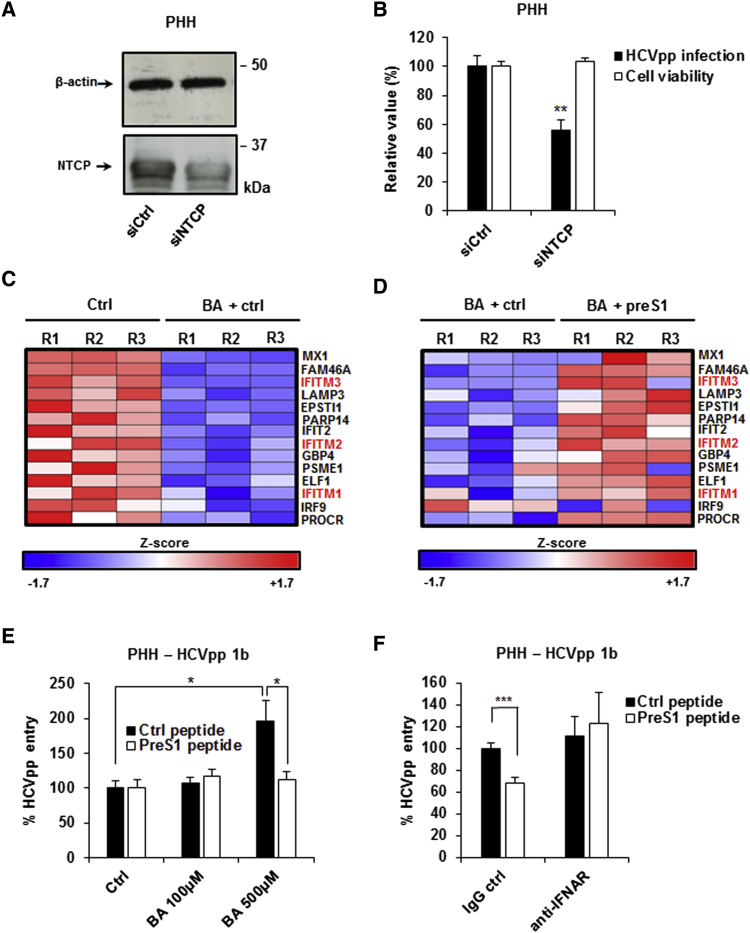
Figure 6.
NTCP-Mediated Bile Acid Uptake Modulates ISG Expression and HCV Entry in PHHs
(A and B) Silencing NTCP expression in PHHs. PHHs were transfected with siRNA control (siCtrl) or siRNA targeting NTCP (siNTCP). 3 days after transfection, siRNA efficacy was assessed by western blot (A), and cell viability was assessed using PrestoBlue reagent (B). Results are expressed as means ± SEM percentage cell viability compared to cells treated with siCtrl from two independent experiments performed in quintuplicate (n = 10) (B). 3 days after NTCP silencing, PHHs were incubated with HCVpp (genotype 1b). Infection was assessed after 72 hr by measuring luciferase activity. Results are expressed as means ± SEM percentage HCVpp entry from three independent experiments performed in triplicate (n = 9) (B).
(C and D) Bile acids modulate the expression of ISGs in PHHs. PHHs from a single donor were treated with the bile acid (BA) sodium taurocholate (500 μM) in the presence or absence of the preS1 peptide (400 nM) for 48 hr. Cells were then lysed and total RNA was extracted and purified. Total gene expression was analyzed by genome-wide microarray. Three independent biological replicates per condition were analyzed. (C) Individual IFNα response genes that are significantly (p < 0.05) repressed following BA treatment are shown. Individual Z scores for each sample are presented. Negative Z score (blue) and positive Z score (red) correspond to repression and induction of the indicated genes, respectively. (D) Effect of preS1 treatment on the expression of IFNα response genes presented in (C). Individual Z scores for each sample are presented.
(E) Effect of bile acid and preS1 treatment on HCVpp infection in PHHs. PHHs were treated with increasing concentrations (0, 100, and 500 μM) of BA in the presence of either preS1 or Ctrl peptide (400 nM) for 72 hr and then infected with HCVpp (genotype 1b). Infection was assessed after 72 hr by measuring luciferase activity. Results are expressed as means ± SEM percentage HCVpp entry compared to untreated PHHs in the presence of the control peptide (set at 100%) from four independent experiments performed in triplicate (n = 12).
(F) PreS1 inhibition of HCVpp entry is dependent on the IFN-signaling pathway in PHHs. PHHs were treated with 500 μM BA in the presence of preS1 or a scrambled control peptide (400 nM), with or without treatment with an antibody targeting the type I IFN receptor (IFNAR) for 72 hr. Cells were then infected with HCVpp (genotype 1b) and infection was assessed after 72 hr by measuring luciferase activity. Results are expressed as means ± SEM percentage HCVpp entry compared to PHHs treated with the control peptide and an IgG control (set at 100%) from three independent experiments (one performed in triplicate and two in quintuplicate; n = 13).