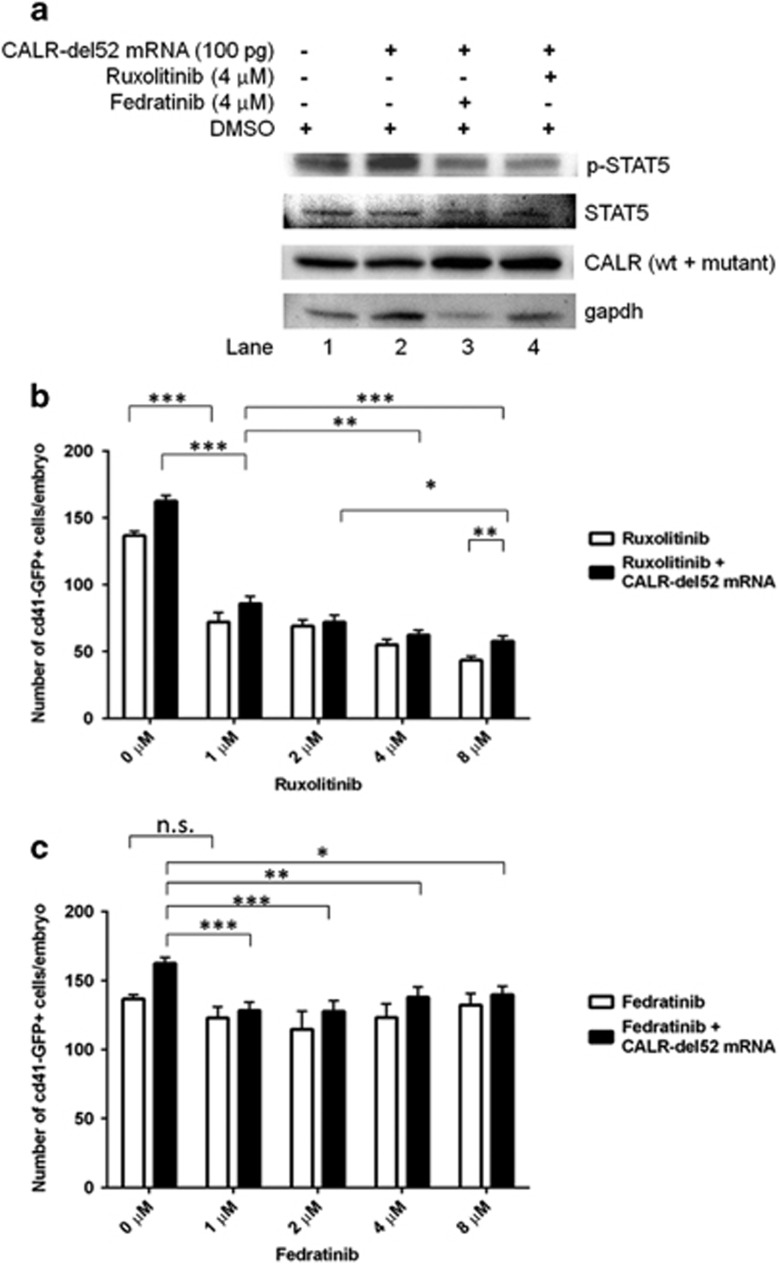
Figure 4.
The expression of mutant CALR activates jak-stat signaling in zebrafish. (a) Western blotting showing embryos of wild-type zebrafish injected with CALR-del52 mRNA (100 pg) have significantly increased signal transducer and activation of transcription (stat) 5 phosphorylation (lane 2) as compared with uninjected control embryos from the same batch at 24 h.p.f. (lane 1). Pharmacologic treatment of embryos with a JAK2-selective inhibitor (fedratinib) and a dual JAK1/JAK2 inhibitor (ruxolitinib) significantly attenuated the enhanced stat5 phosphorylation induced by CALR-del52 mRNA stat5 phosphorylation (lane 3 and 4, respectively). Total amount of stat5 protein was not affected in all experiments. (b and c) Effects of the pharmacologic treatment with ruxolitinib and fedratinib (from 1 μM to 8 μM) on the numbers of CD41+ thrombocytes at 5 d.p.f. with or without the injection of CALR-del52 mRNA. Treatment with ruxolitinib significantly decreases the numbers of CD41+ thrombocytes in uninjected control as well as CALR-del52-injected embryos in a dose-dependent manner. Whereas treatment with fedratinib has minimal and insignificant inhibitory effect on the number of CD41+ thrombocyte in uninjected control embryos, and has a modest and significant dose-independent inhibitory effect on mutant CALR-induced thrombocytosis (n.s., not significant; *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001; Student t-test).