Figure 1.
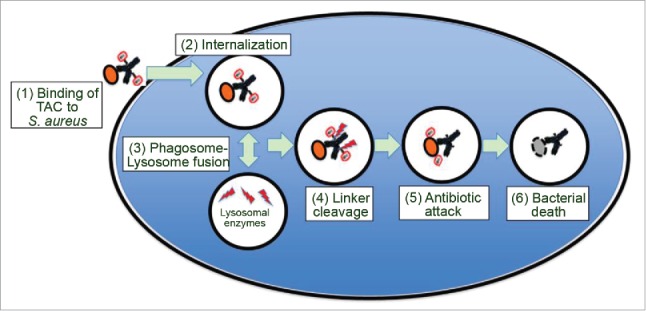
Model for the mechanism of action of TAC. As depicted in the model, (1) TAC binds to S. aureus bacteria, (2) TAC bound S. aureus bacteria are internalized by professional phagocytes or other host cells such as epithelial cells. After (3) phagosome-lysosome fusion, (4) lysosomal cathepsins cleave the linker, which (5) releases the active antibiotic dmDNA31 attacking the intracellular bacteria, resulting in (6) elimination of the bacteria.
