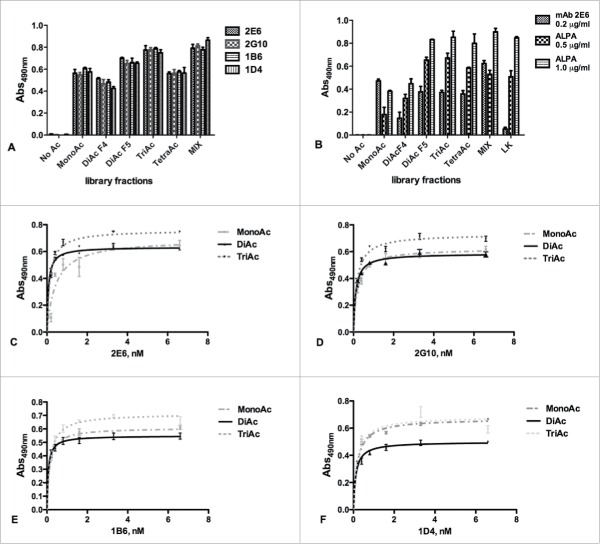
Figure 2.
(A) Screening of the HPLC fractions containing differently acetylated APE1 peptides using the 4 mAbs (2E6, 2G10, 1B6, 1D4) previously shown to discriminate between the acetylated and non-acetylated peptides (Fig. SM1). The antibodies appeared more specific for the mono-acetylated, di-acetylated (fraction 5) and tri-acetylated peptides. Also the non-acetylated peptide and the restored MIX of all molecules were used as control. Experiments were performed as quadruplicate and expressed as value ± standard deviation (sd). (B) Binding of 2E6 and ALPA antibodies to the APE1-derived acetylated peptides. As expected, no binding was detected for the non-acetylated molecule for both antibodies, whereas ALPA binding correlated with the extent of peptide acetylation. Experiments were performed as triplicate and expressed as values ± sd. Dose-dependent binding assay of 2E6 (C), 2G10 (D), 1B6 (E), 1D4 (F) antibodies to the fractions containing the APE1- derived mono-, di-, and tri-acetylated peptides. Concentrations ranged between 0.2 and 6.6 nM. The extrapolated apparent KDs are reported in Table S2.