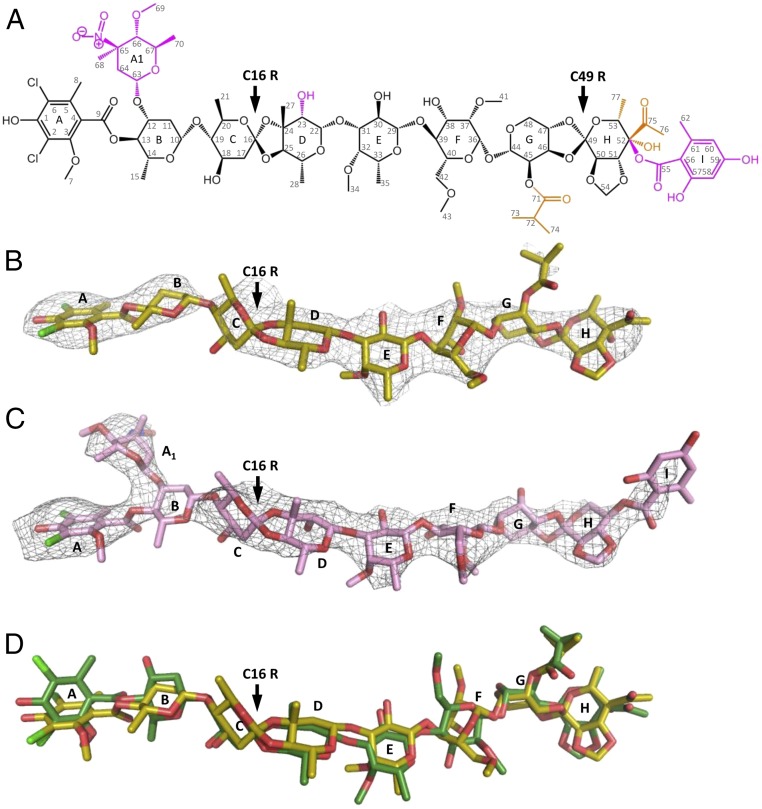
Fig. 1.
(A) The orthosomycin family consists of a common DIA residue (res A) and a heptasaccharide (residues B–H) shown in black, and two orthoester linkages at C16 and C49 pointed by an arrow. The heptasaccharide chain consisting of d-olivose (residues B and C), 2-deoxy-d-evalose (residue D), 4-O-methyl-d-fucose (residue E), 2,6-di-O-methyl-d-mannose (residue F), l-lyxose (residue G), and eurekanate (residue H). The additional chemical substitutes of avilamycin and evernimicin on the heptasaccharide chain are shown in orange and magenta, respectively. Evernimicin possess an additional l-evernitrose (res A1), orsellinic acid (res I), and a hydroxyl group on residue D. (B and C) Weighted 2Fo–Fc difference Fourier map contoured at 1σ of avilamycin (yellow) and evernimicin (pink) in complex with D50S. (D) Avilamycin conformation in D50S–avi complex (yellow) and free avi (green) superposed.