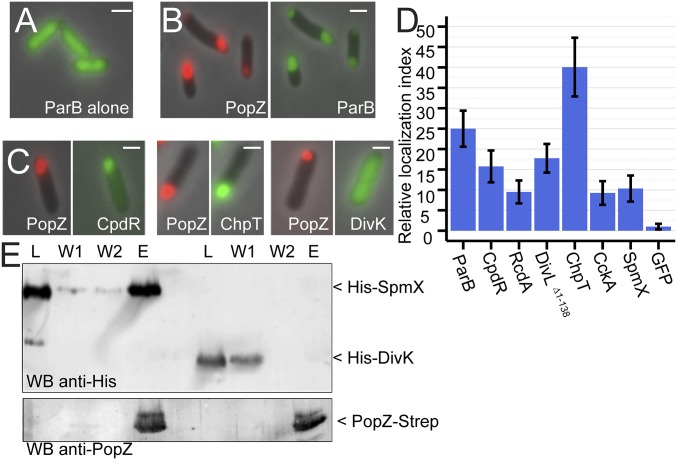
Fig. 1.
Interactions between PopZ and binding partners. (A) Localization of ParB-GFP (green) when expressed independent of PopZ in E. coli. (B) Localization of ParB-GFP (green, Right) when coexpressed with mChy-PopZ (red, Left) in E. coli. (C) mChy-PopZ exhibits selective recruitment of Caulobacter proteins in this assay. (D) The polar localization of each GFP-tagged candidate protein was normalized with respect to free GFP and plotted as a “relative localization index.” (E) Direct interaction between PopZ and SpmX in vitro. Purified 6His-SUMO-SpmX or 6His-SUMO-DivK (lane L) was passed through a column with PopZ bound to the matrix. After washing (lanes W1 and W2), PopZ and other bound proteins were eluted (lane E). (Scale bars, 1 μm.)