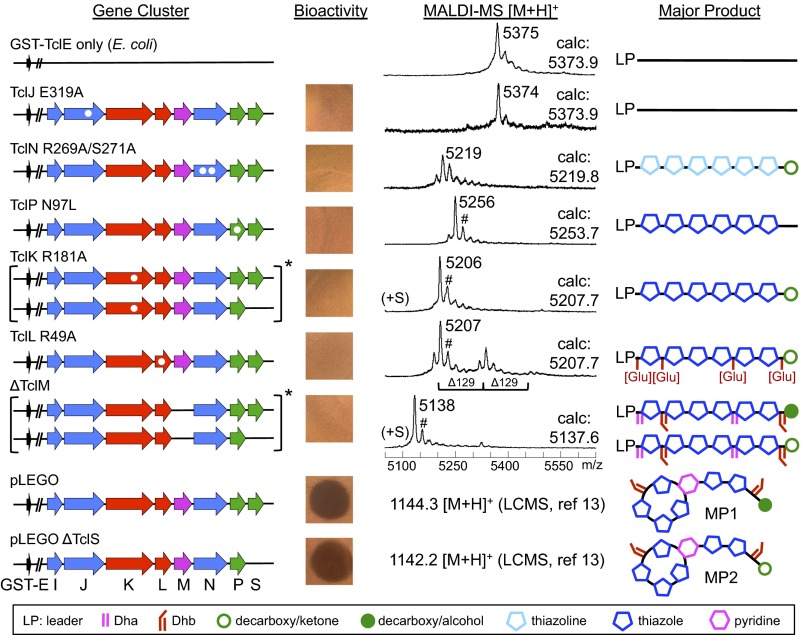
Fig. 3.
Dissection of micrococcin biosynthesis by genetic disruption, capture of biosynthetic intermediates, and mass analysis. Amino acid substitutions are indicated with white dots within tcl genes (arrows). Bioassays of methanol extracts from each strain are shown along with MALDI-MS data for modified peptides obtained after TEV-cleavage of GST-tagged intermediates. Observed m/z values are given next to major peaks, and calculated m/z values (calc) are indicated. Products consistent with mass values of the major peaks are diagrammed on the right, with chemical group symbols shown in the accompanying key. Asterisk (*) denotes mass comparisons that required high-resolution ESI-LCMS (see Fig. 4). Nonproton adduct ions were observed (#) and found to be +17 amu via ESI-LCMS. Previous studies showed only MP1 is produced from the full set of genes, whereas only MP2 is formed in the ∆TclS strain (13).