Figure 3.
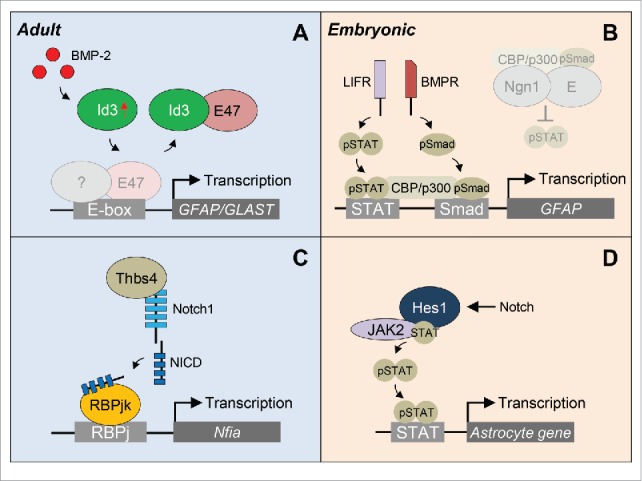
Proposed models of transcriptional regulation of NSPC differentiation into astrocytes. (A) After traumatic brain injury, elevated BMP-2 levels in the SVZ are translated into an increase in Id3 expression. Id3 then heterodimerizes with E47 and prevents the E47-mediated repression of astrocyte-specfic genes GFAP and GLAST. (B) During embryogenesis, pro-neurogenic Ngn1 inhibits astrogenesis by preventing STAT phosphorylation and occupying the CBP/p300 cofactor complex (gray shadow), the latter synergistically bridging the STAT and Smad signaling pathways. When neurogenesis is completed, Ngn1 is downregulated and in the absence of Ngn1, pSTAT recruits the CBP/p300-pSmad complex to the promoter to activate GFAP gene expression. (C) Focal stroke increases the number of Thbs4+ SVZ-born astrocytes. Thbs4 binds directly to the Notch1 receptor activating Notch signaling and expression of the Nfia transcription factor important for astrocyte differentiation. (D) During embryogenesis, Notch effector Hes1 associates with JAK2 and STAT to facilitate JAK-STAT complex formation, thus promoting STAT phosphorylation and astrocyte gene expression. BMPR, BMP receptor; LIFR, LIF receptor; NICD, Notch intracellular domain.
