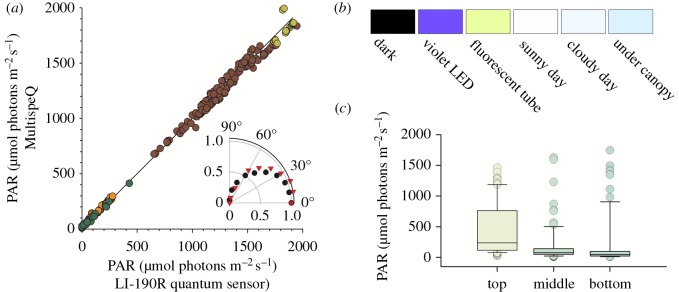
Figure 2.
Comparing measurements of PAR sensor implemented in the MultispeQ against a LI-COR LI-190R Quantum Sensor. (a) The sensors were compared under different light qualities, natural full sunlight (yellow circles), cloud coverage (brown circles), under a plant canopy (orange circles) and with red (630 nm emission), green (535 nm), violet (435 nm) or white emitting LEDs (green circles). MultispeQ measurements were corrected, solving the following equation, based on the intensities from the sensors four channels, red, green, blue and white (PAR = white × 0.65847 + red × −1.60537 + green × −2.30216 + blue × −0.50019). The device specific coefficients are derived using a pseudo-inverse matrix equation including the four channels and the corresponding PAR values from the LI-COR PAR sensor. Inset: normalized light intensity measurements for both sensors as a function of illumination angles (black circles, LI-COR 190R; red triangles, MultispeQ). (b) Colours based on the intensities measured for the red, green and blue channel under different light conditions. (c) Light quality dependence on positions in the canopy of a Miscanthus giganteus field on one day in August, early afternoon. The fact that the measurements were time- and geo-tagged through the PhotosynQ platform allowed us to determine that the sky was partially cloudy (http://forcast.io), contributing to the variable illumination. The canopy was approximately 3 m in height, and leaf positions were chosen for measurements near the top (within 30 cm of the top of the plant) middle (approx. 1.5 m from ground) and bottom (approx. 50 cm from ground). The mean and standard deviation of the light intensities are indicated by the box and whiskers plot and the light quality reproduced as the colour of the filled boxes and circles.