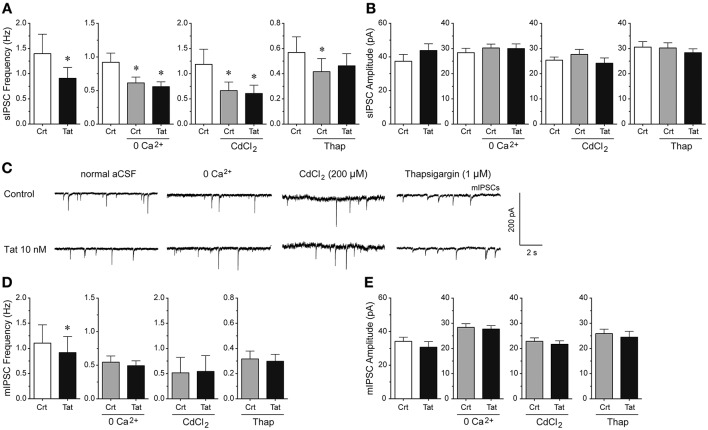
Figure 4.
Extracellular and intracellular calcium contribute to the significant Tat (10 nM) effects on the mean frequency of IPSCs. (A) The significant Tat (10 nM) effect on the mean frequency of sIPSCs (n = 13 neurons) was blocked by zero extracellular Ca2+ (n = 13 neurons), CdCl2 (200 μM, n = 10 neurons), and thapsigargin (1 μM, n = 10 neurons). (B) No Tat effects were noted on the mean amplitude of sIPSCs. (C) Representative traces show sIPSCs before and after application of Tat (10 nM) in the presence of normal aCSF, zero extracellular Ca2+, CdCl2 (200 μM), and thapsigargin (1 μM). (D) The significant Tat (10 nM) effect on the mean frequency of mIPSCs (n = 15 neurons) was blocked by zero extracellular Ca2+ (n = 8 neurons), CdCl2 (200 μM, n = 9 neurons), and thapsigargin (1 μM, n = 10 neurons). (E) No Tat effects were noted on the mean amplitude of mIPSCs in any condition. Data are mean ± SEM. Significance was assessed by paired Student t-tests. *p < 0.05 vs. Control of corresponding condition. aCSF, artificial cerebrospinal fluid; Crt, Control; Thap, Thapsigargin.