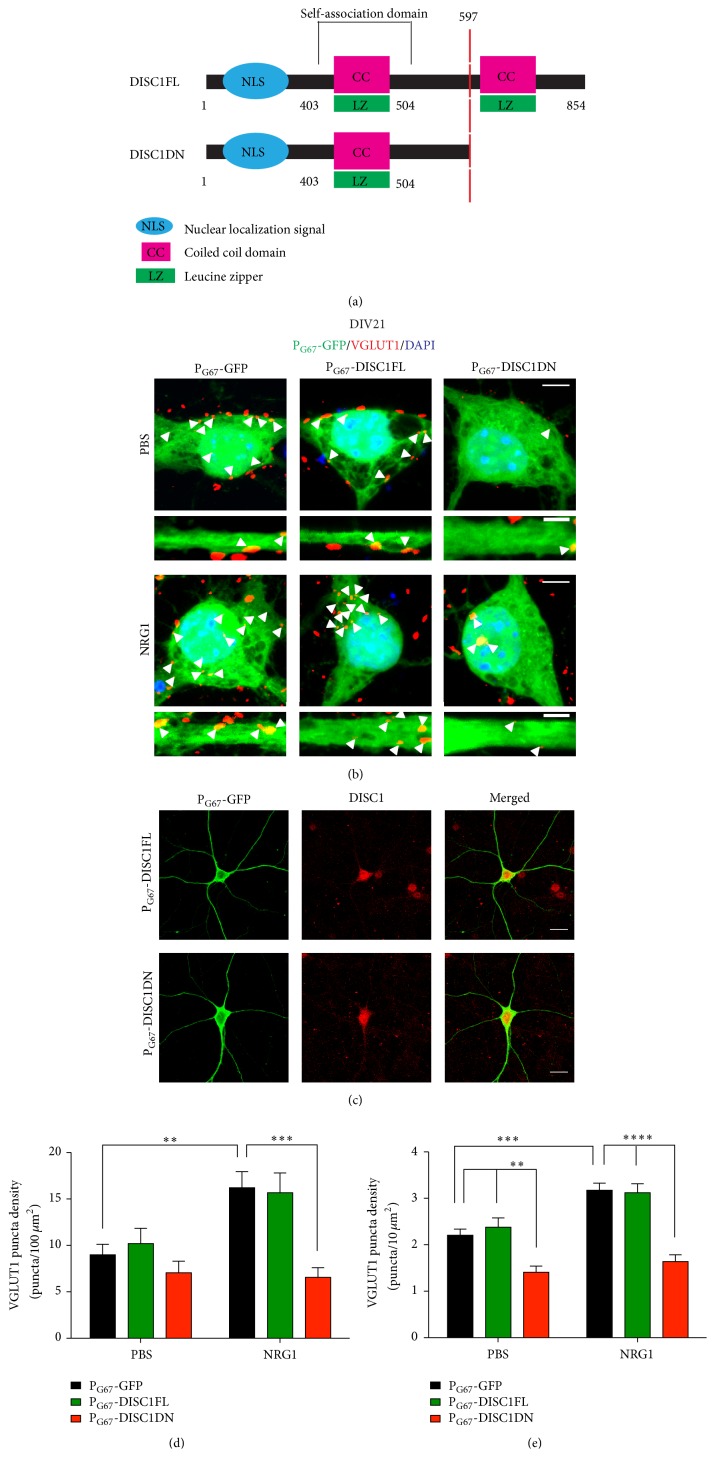
Figure 2.
NRG1 functions through DISC1 to regulate glutamatergic synaptogenesis onto cortical inhibitory neurons. (a) Schematic of the mouse DISC1FL protein and DISC1DN truncated mutant protein. (b) Representative images of immunofluorescence staining of VGLUT1 in DIV21 cortical inhibitory neurons cotransfected with PG67-GFP and PG67-DISC1FL or PG67-DISC1DN on DIV7. Cells were treated with NRG1β or PBS for 2 days. Cultures were stained for GFP to enhance the GFP signal. Images were acquired at 63x. Scale bars = 5 μm (cell body zoom image), 2 μm (dendrite zoom image). Arrowheads indicate VGLUT1 puncta colocalized with PG67-GFP. (c) Representative images of immunofluorescent staining of DISC1 in DIV21 cortical inhibitory neurons transfected with PG67-GFP and PG67-DISC1FL or PG67-DISC1DN on DIV7. NRG1β treatment caused a significant increase in VGLUT1 puncta density in the cell body (d) and primary dendrites (e) which was blocked by expression of PG67-DISC1DN. Significance determined using a one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Tukey's post hoc tests. Error bars represent standard error of the mean, n = 27–50 cells (2-3 primary dendrites/cell) per condition from 3 experiments, ∗∗ p < 0.01, ∗∗∗ p < 0.001, and ∗∗∗∗ p < 0.0001.