Figure 2.
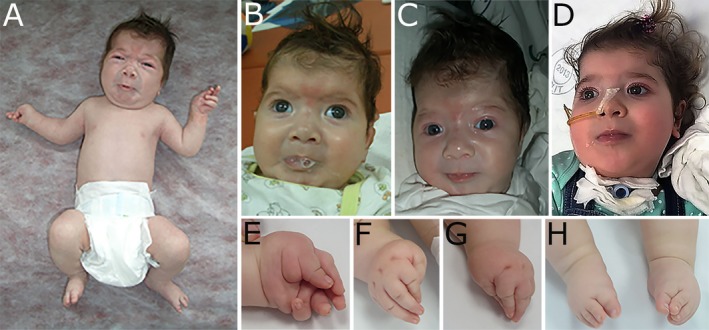
Typical facial characteristics of CLIFAHDD syndrome are shown in (A–C): broad nasal bridge, anteverted nasal tip and large nares, short columella, long philtrum, deep nasolabial folds, rounded cheeks, pursed lips, micrognathia, H‐shaped chin dimpling, low‐set ears, and short neck. (A) Illustrates the stimulus‐provoked facial and limb contractions, particularly frequent in the neonatal period; arms are flexed and abducted, legs flexed or cycling. Mild contractures were present at elbows, knees, and hips. (B) Copius foamy saliva extrudes from the pursed lips. (C) During the attack, the child sweats excessively in the face, head and upper trunk. (D) At age 33 months: the child is anxious, facial contractions are milder, drooling persists; she is dependent on nasogastric tube feeding and is treated with positive pressure ventilation via tracheostomy. (E–G) illustrate the distal arthrogryposis; with camptodactyly, adducted thumbs, and ulnar deviation. (H) Bilateral varus foot deformity.
