Figure 2.
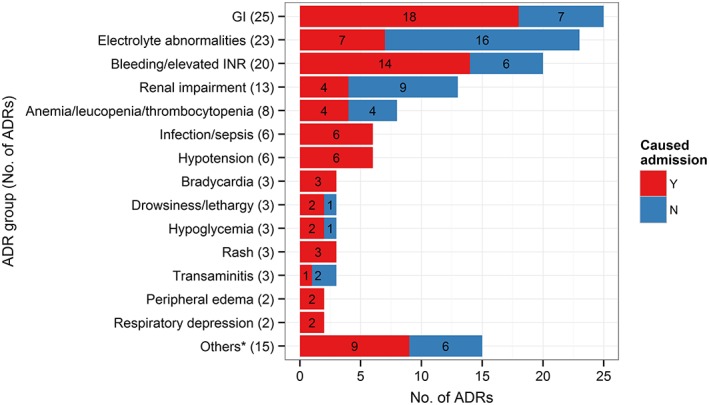
Most common ADRs. The figure shows the number of ‘definite’ and ‘probable’ ADRs grouped by ADRs. GI ADRs included nausea, vomiting, abdominal bloatedness, diarrhoea, constipation and dyspepsia. Electrolyte abnormalities included high or low serum sodium, potassium, magnesium, phosphate or calcium levels. *Acute gout flare, cytomegalovirus reactivation/viraemia, elevated creatine kinase, elevated haemoglobin, elevated T4/suppressed thyroid stimulating hormone, extrapyramidal side effects, headache, elevated white cell count, lactic acidosis, mucositis, peripheral neuropathy, premature ventricular complex, QTC prolongation, seizure and tremors (1 each). ADR: adverse drug reaction, GI: gastrointestinal, INR: international normalized ratio
