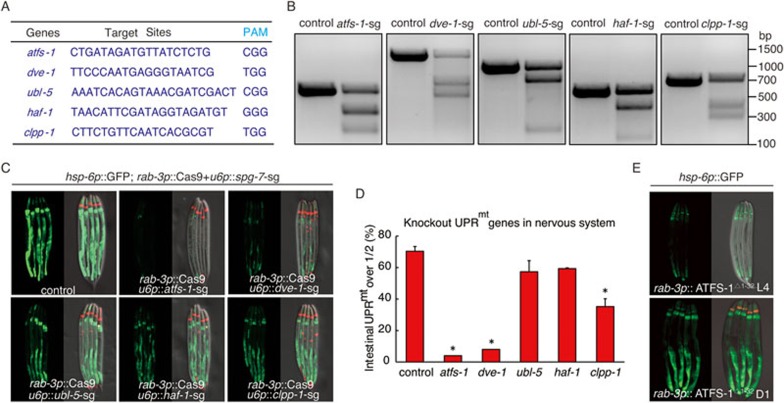
Figure 5.
A functional UPRmt pathway in neurons is required for peripheral induction of UPRmt. (A) Targeting sequences of UPRmt pathway genes for CRISPR-Cas9 knockout, together with their PAM sequences. (B) Deletions of UPRmt pathway genes produced by CRISPR/Cas9 are detected by T7E1 assay. Representative DNA gels of T7E1 assay reveals the PCR products amplified from genomic DNA of control worms, or worms with UPRmt pathway gene deletion in the nervous system. (C, D) Neural knockout of atfs-1 or dve-1 suppresses the UPRmt in distal tissues in rab-3p::Cas9+u6p::spg-7-sg worms. Representative fluorescent images (C) and quantification of hsp-6p::GFP reporter expression (D) in animals containing rab-3p::Cas9+u6p::spg-7-sg (control) or rab-3p::Cas9+u6p::spg-7-sg with neural-specific knockout of UPRmt genes are shown. mec-7p::RFP is used as co-injection marker. n ≥ 28, error bars indicate mean ±SE. A Student's t-test is used to assess significance: *P < 0.05. (E) Neural expression of ATFS-1Δ1-32 induces UPRmt in distal tissues when worms reach day 1 adult stage. odr-1 p::dsRed is used as co-injection marker.