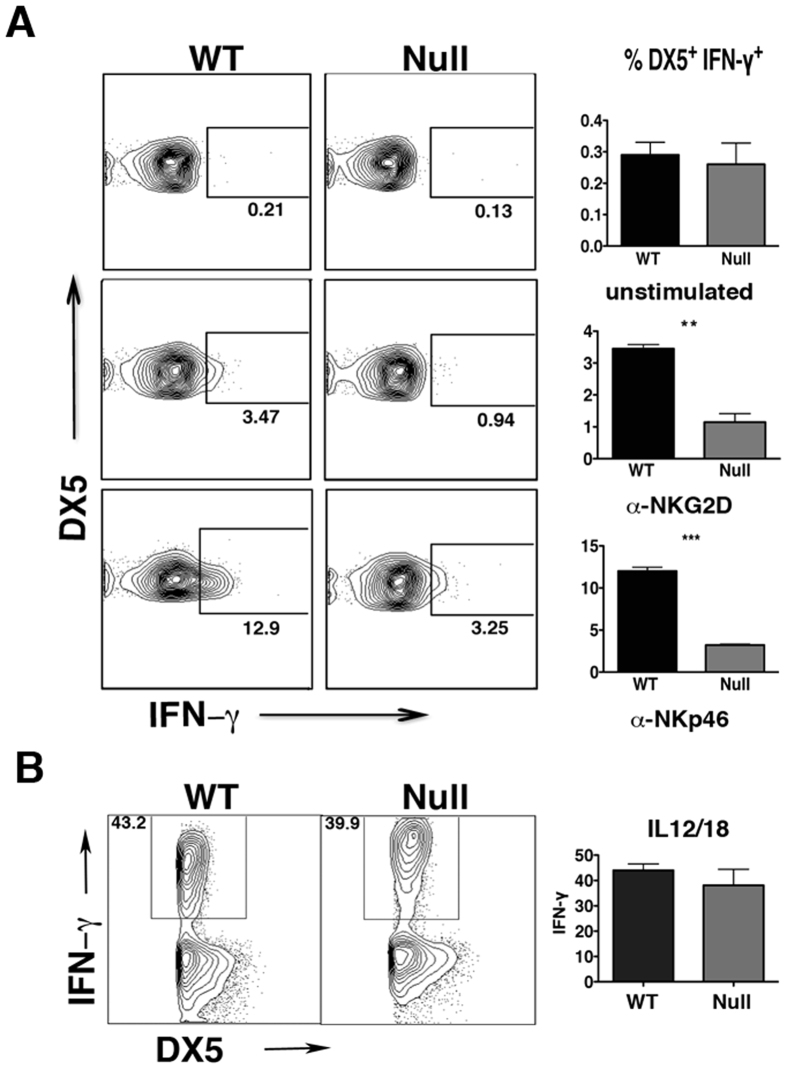
Figure 3. LRBA is required for NK activating receptors to induce IFN-γ.
(A) Splenocytes from WT and Null mice, injected with polyI:C were stimulated with 50μg of plate-bound α-NKp46 or α-NKG2D antibodies. The induction of IFN-γ was analyzed by intracellular cytokine staining. Plots show the frequency of IFN-γ + NK cells after gating on CD49b(DX5)+ TcRβ− cells. (B) Splenocytes from unmanipulated WT and LRBA-null mice were stimulated overnight using IL12 and IL18. The production of IFN-γ was then analyzed by flow cytometry. Statistical analysis of LRBA-null and WT NK cell production of IFN-γ showed no significant difference (p = 0.4). Results are representative of three independent experiments (A-B). **p < 0.05, ***p < 0.0001.