Figure 1.
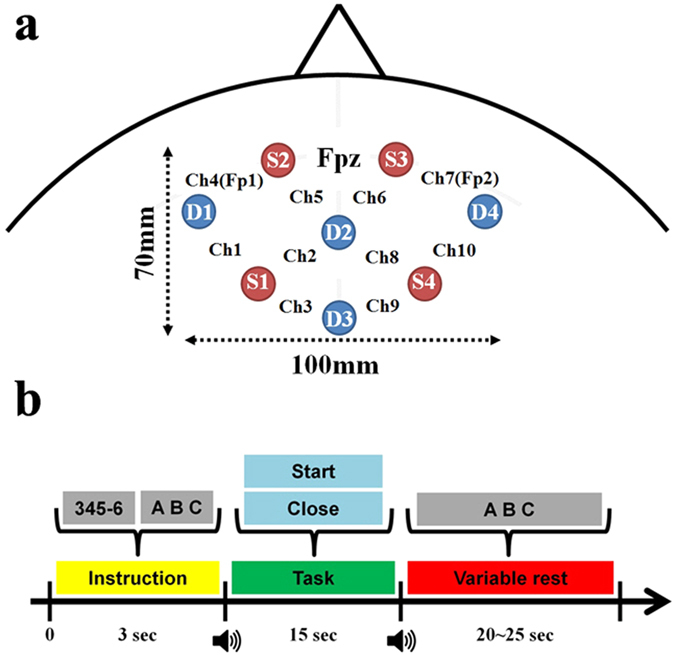
(a) Placement of NIRS source and detector optodes. Red (S1-4) and blue (D1-4) circles indicate the locations of source and detector optodes, respectively. NIRS channels are located between pairs of sources and detectors. Channels 1–5 and 6–10 are located on the left and right hemisphere, respectively. Channels 4 and 7 are placed on the Fp1 and Fp2 according to the international 10–10 system, respectively. (b) EO and EC paradigms. During an instruction, a task that the subject should perform is displayed for 3 s, e.g., 345–6 for mental arithmetic (MA), ABC for imagined vocalization of the English alphabet as a baseline task (BL). For MA, a pair of a three-digit (100–999) and one-digit (6–9) numbers are randomly displayed and varied for each trial. For the EC paradigm, the subject is asked to close his/her eyes as soon as he/she knows which task (either MA or BL) will be performed during the instruction period. The task period starts with a short beep sound. For the EO paradigm, the word ‘Start’ is displayed and the subject starts performing a given task. For the EC paradigm, ‘Close’ is displayed during the task period but the subject cannot see the word because the subject already closed the eyes before the presentation of ‘Close’. After a task period of 15 sec, a variable rest period starts with another beep sound during which the word ‘ABC’ is displayed. For the EO paradigm, the subject starts imagined vocalization of the English alphabet as controlled rest, while the subject first opens his/her eyes as soon as he/she hears the beep sound and starts imagined vocalization of English alphabet for the EC paradigm. Note that the imagined vocalization is used for both BL and controlled rest in the rest period.
