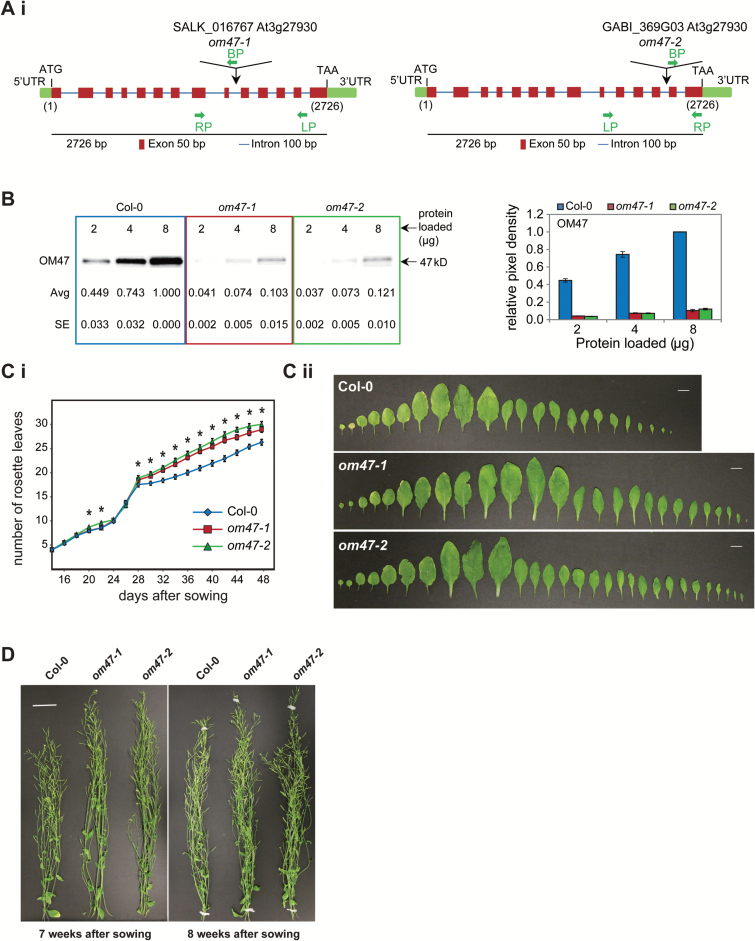
Fig. 3.
Confirmation and characterization of T-DNA insertional knock-out lines for Arabidopsis thaliana OM47. (A) Diagram illustrating the positions of the T-DNA inserts in (i) om47-1 (SALK_016767) and (ii) om47-2 (GABI_369G03) lines of the A. thaliana OM47 (At3g27930) gene. Also shown is the length (bp), UTRs (untranslated regions), ATGs (start codon), TAAs (stop codon), exons (red squares), and introns (blue lines) of the OM47 (At3g27930) gene (see Supplementary Fig. S1 for the exact site of T-DNA inserts). LP, RP, and BP represent the primers used for screening the T-DNA insertions (see Supplementary Table S1 for specific primer sequences). (B) SDS–PAGE (left panel) and quantified relative pixel density (right panel) showing OM47 proteins in mitochondria isolated from 2-week-old A. thaliana wild type (Col-0), om47-1 (SALK_016767), and om47-2 (GABI_369G03). The amounts of mitochondrial protein loaded and apparent molecular mass of the protein detected (47kDa) are indicated. Serial dilutions of mitochondrial proteins were used to ensure linearity of detection, and immunodetection was carried out in biological triplicate, with numbers giving averages (avg) and SEs. (C) (i) The two om47 mutant lines had an increased number of leaves from ~8 d after sowing when compared with the wild type (Col-0) which was maintained through later stages of development. (ii) A series of developmental stages of all leaves from the 7-week-old wild type and om47 mutants reveals the increased number of leaves in the two mutant lines. In addition, the oldest leaves of the wild type show an earlier onset in senescence when compared with the mutants. (D) At late developmental stages (7 and 8 weeks after sowing), both om47 mutant lines had a higher inflorescence than the wild type.