Figure 5. Experiment 2: Abrupt adaptation.
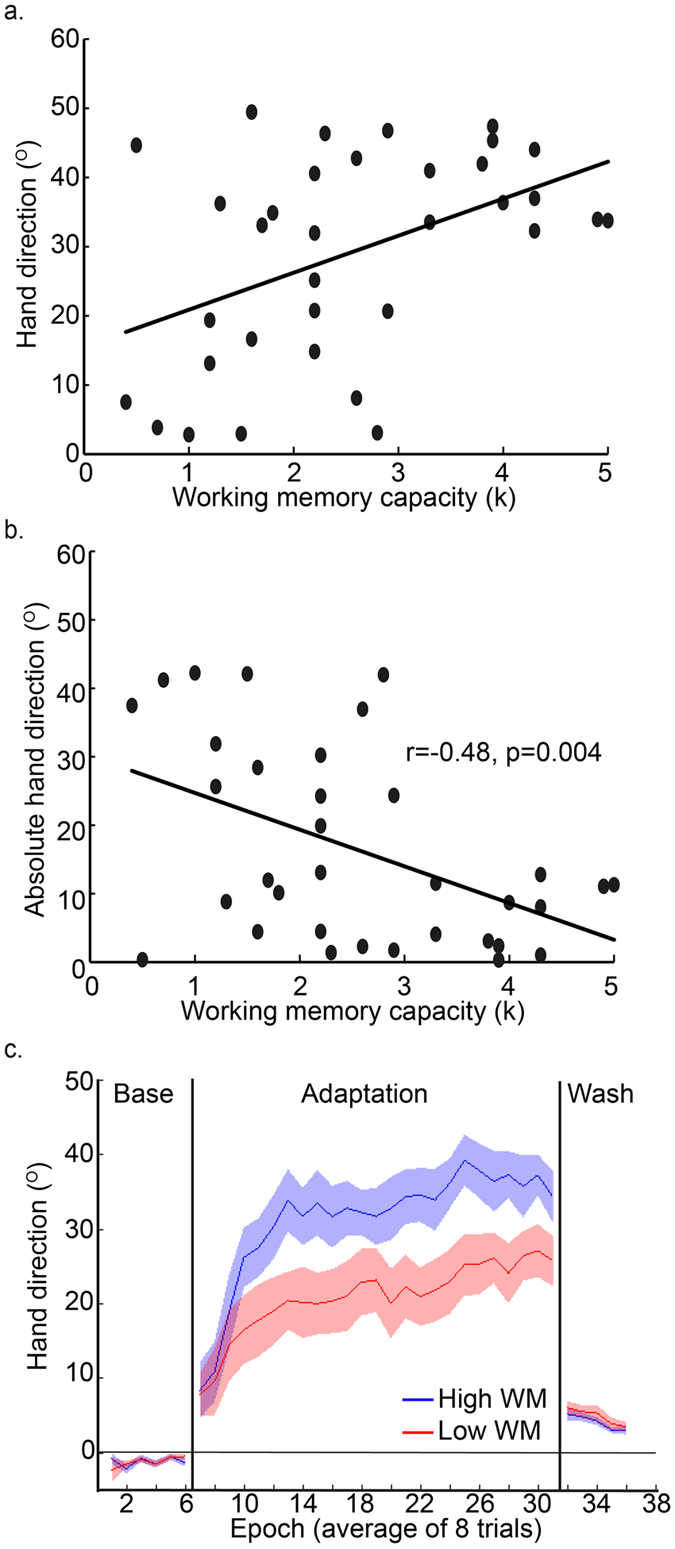
(a,b) The significant correlation between WMC and hand direction (a) and between WMC and absolute hand direction error (b) during adaptation to an abrupt 45° visuomotor rotation when participants did not report their hand direction. (c) For illustration we performed a median split, separating the group into those with high and low WMC. Hand direction throughout the experiment is shown for the high WMC (n = 17, blue) and low WMC (n = 17, red) groups (line = group mean, shaded area = standard error of mean across group). The high WMC group showed greater adaptation relative to the low WM group, however no differences were observed during baseline or washout.
