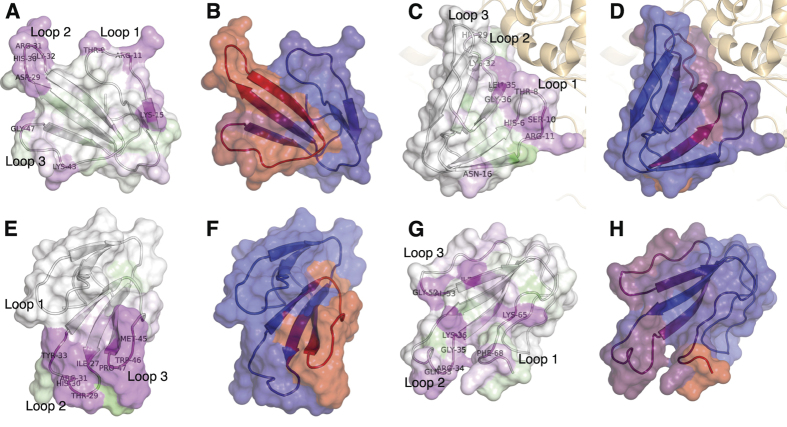
Figure 5. Structural presentation of B-cell epitope analysis.
(A,B) Short neurotoxin 1 (P01416) from D. polylepis as an example of a type 1 α-neurotoxin. Structure built upon54; (C,D) Fasciculin-2 (P0C1Z0) from D. angusticeps as an example of a fasciculin. The Fasciculin-2 is co-crystallised with the human acetylcholinesterase enzyme. Structure built upon55; (E,F) Toxin FS-2 (P01414) from D. polylepis as an example of an L-type calcium channel blocker. Structure built upon35; (G,H) Alfa-elapitoxin-Dpp2c (P01397) from D. polylepis as an example of a type 2 α-neurotoxin. Structure built upon56. (A,C,E,G) Residues coloured according to alanine substitution effect in log2 fold-change, where magenta indicates that a residue is of particular importance for antibody recognition. Residue numbers refer to original sequence and not alignment; (B,D,F,H) Residues coloured according to residue score, where dark red refers to resides with high residue score, and blue refers to residues with low residue scores.