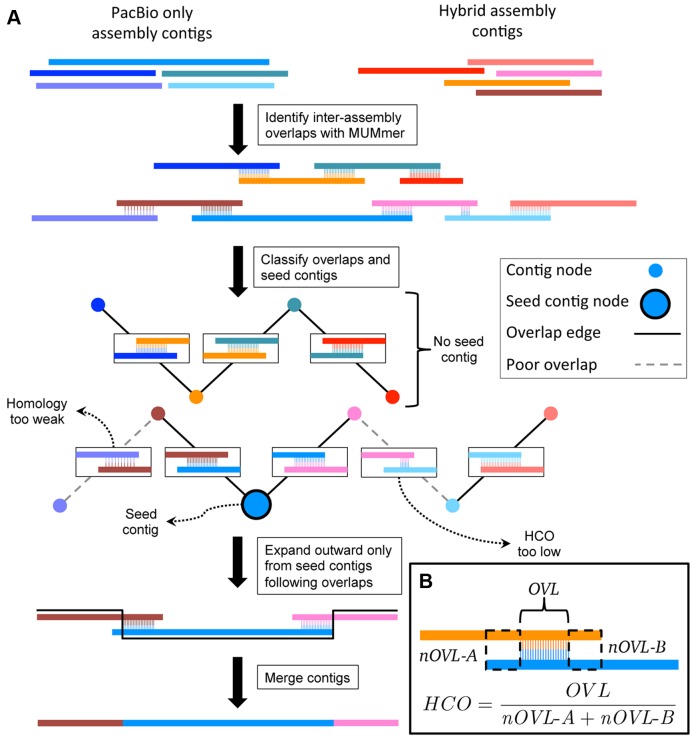
Figure 4.
(A) A diagram representing the algorithm employed by quickmerge to improve genome contiguity. (A) MUMmer is used to identify overlaps between the two assemblies. High confidence overlaps (HCOs) identified by MUMmer will be the primary signal to quickmerge that two contigs should be joined. Quickmerge clusters contigs according to HCOs. Quickmerge identifies seed contigs (contigs in a cluster above a certain size and HCO), and identifies a path that connects it to all other contigs in its cluster by walking from one contig to the next, only stepping to the next contig if the quality of the HCO between the current and next contigs is above the set thresholds. Once the graph connecting available contigs to the seed contig has been constructed, the contigs in the graph are spliced together, with the ‘Donor’ genome's content preferred over the ‘acceptor’ genome. (B) Description of the HCO parameter. HCO represents the ratio between overlapping aligned and overlapping unaligned parts between two contigs.