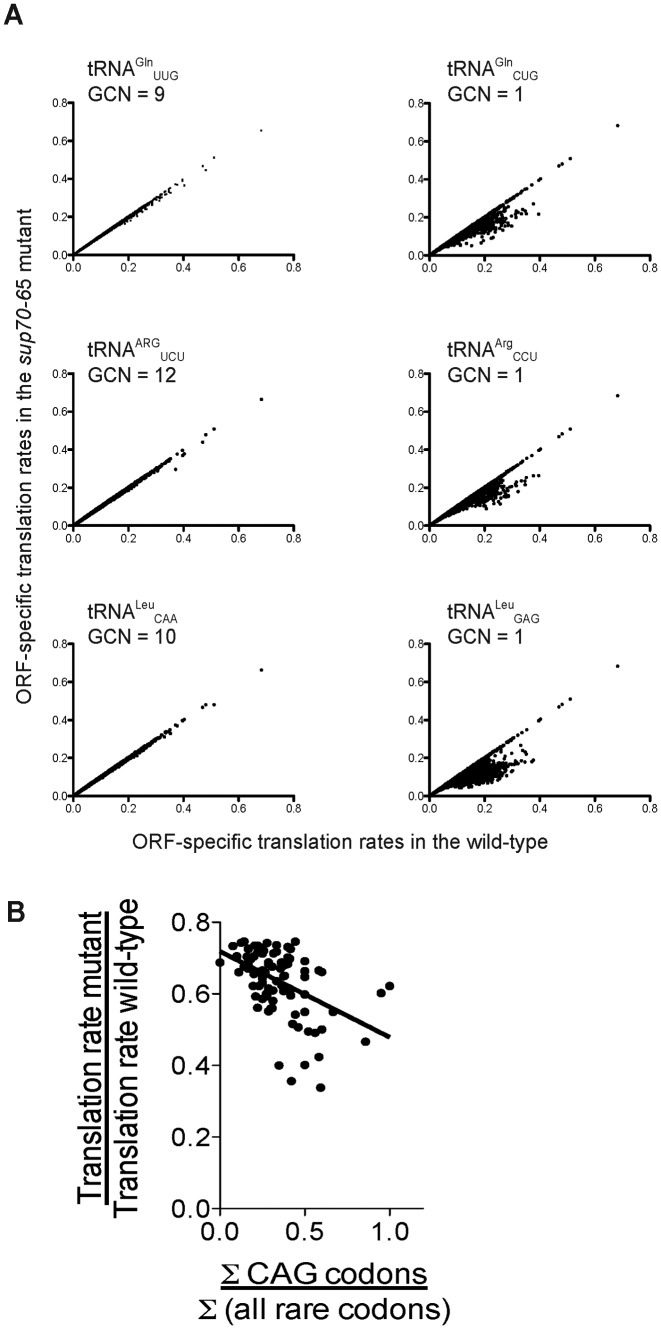
Figure 7.
Translation is sensitive to changes in concentrations of rare tRNAs. (A) Translation of all 5500 yeast ORFs was simulated using the TASEP model representing a wild-type spectrum of tRNA concentrations, and again for a simulated cell where the concentration of one tRNA type was reduced to 25% of wild-type levels. The wild-type translation rate for each ORF is plotted against the corresponding tRNA-depleted rate. This exercise was repeated for all 42 species of yeast cytoplasmic tRNA. The results for 6 tRNAs are presented, three types whose encoding genes are multicopy (Gene Copy Number GCN > 4; left column), and three single gene-copy tRNAs (GCN = 1; right column). (B) A disproportionately high content of CAG codons within an ORF, relative to other rare codons, together with the configuration of those CAG codons, may drive ORF sensitivity to 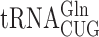 concentrations. To test this, for the 90 most sup70-65 sensitive ORFs, the CAG rare codon content, normalised to content of other rare codons, was plotted against the translation efficiency ratio (sup70-65/wild-type) revealing a negative correlation (R2 = 0.21).
concentrations. To test this, for the 90 most sup70-65 sensitive ORFs, the CAG rare codon content, normalised to content of other rare codons, was plotted against the translation efficiency ratio (sup70-65/wild-type) revealing a negative correlation (R2 = 0.21).