Figure 3.
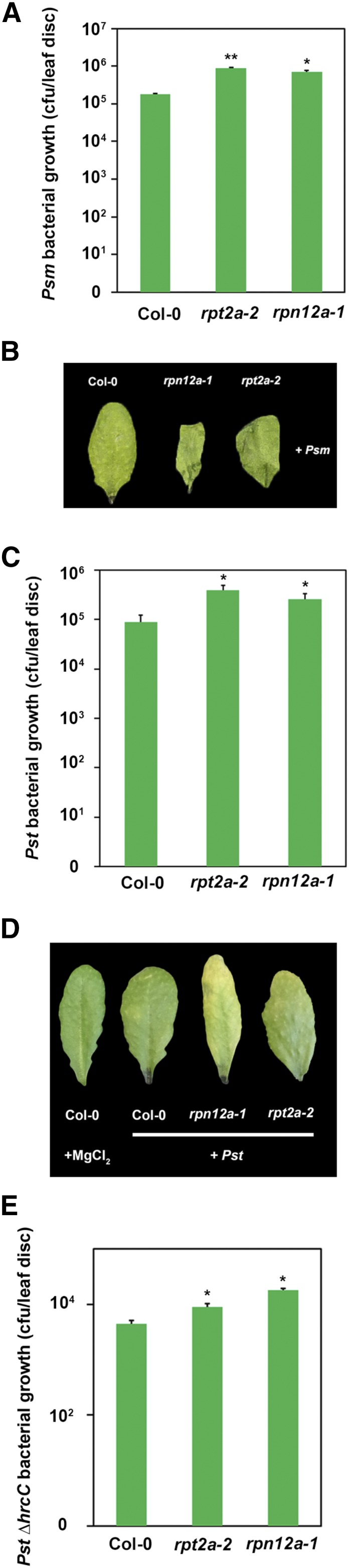
Arabidopsis mutant lines defective in different proteasome subunits display enhanced susceptibility toward infection with Pst and Psm. A, Bacterial density in leaves of different Arabidopsis genotypes infected with Psm. Leaves were syringe infiltrated with 1 × 105 colony-forming units (cfu) mL−1 bacteria, and bacterial multiplication was determined at 2 dpi. Each bar represents the mean of three biological replicates ± sd. Asterisks indicate statistical differences according to Student’s t test (**, P < 0.01 and *, P < 0.05). B, Phenotypes of Psm-infected Arabidopsis leaves 2 dpi. C, Bacterial density in leaves of different Arabidopsis genotypes infected with Pst. Leaves were syringe infiltrated with a bacterial suspension of 1 × 105 cfu mL−1, and in planta bacterial populations were determined 2 dpi. Each bar represents the mean of three biological replicates ± sd. Asterisks indicate statistical differences according to Student’s t test (*, P < 0.05). D, Phenotypes of Psm-infected Arabidopsis leaves 2 dpi. E, The bacterial multiplication of an avirulent Pst ∆hrcC strain is enhanced in leaves of Arabidopsis proteasome mutant lines. Leaves were syringe infiltrated with a bacterial suspension of 1 × 105 cfu mL−1, and bacterial multiplication was determined 2 dpi. Each bar represents the mean of three biological replicates ± sd. Asterisks indicate statistical differences according to Student’s t test (*, P < 0.05). Bacterial growth and infection assays were carried out two times with similar results.
