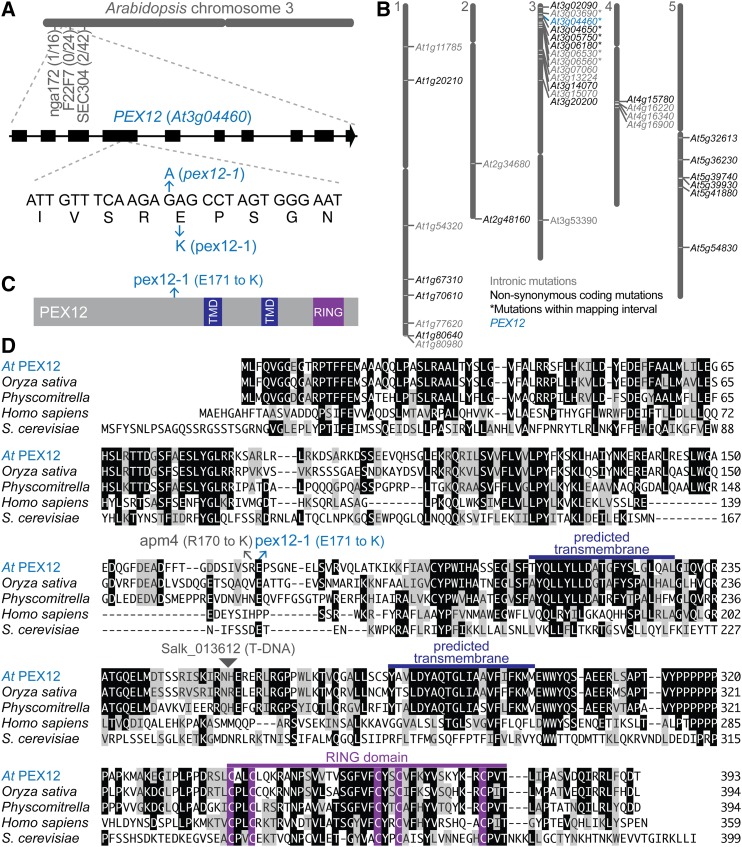
Figure 1.
Identification of pex12-1. A, The causal mutation in an IBA-resistant mutant was mapped to an interval on the top of chromosome 3 that included PEX12 (At3g04460). The number of recombinants at each marker over the number of chromosomes assayed is indicated. A schematic of the PEX12 gene with exons indicated as rectangles and introns as lines is shown above the portion of exon 4 containing the pex12-1 mutation. B, Whole-genome sequencing identified a missense mutation in PEX12. Gene identifiers are shown at their positions on the five Arabidopsis chromosomes for genes containing homozygous mutations consistent with EMS mutagenesis in introns (gray text) or in exons and resulting in nonsynonymous amino acid changes (black or blue text). The seven genes with mutations within the chromosome 3 mapping interval defined in (A) are indicated with asterisks. C, PEX12 protein diagram with predicted transmembrane domains in dark blue, the RING domain in purple, and the position of the pex12-1 Glu171-to-Lys substitution in light blue. D, PEX12 amino acid alignment with the positions of the pex12-1, apm4 (Mano et al., 2006), and a T-DNA insertion line (Salk_013612) conferring embryo lethality (Fan et al., 2005). The MegAlign program (Clustal W; DNASTAR) was used to compare Arabidopsis (At) PEX12 with orthologs from Oryza sativa (Os10g0467200; NP_001064809.1), Physcomitrella patens (XP_001757098.1), Homo sapiens (O00623.1), and Saccharomyces cerevisiae (NP_013739.1). Identical residues in three or more sequences are boxed in black; chemically similar residues are highlighted in gray. The predicted transmembrane domains are marked in dark blue, and the RING domain is highlighted in purple. TMD, Transmembrane domain.