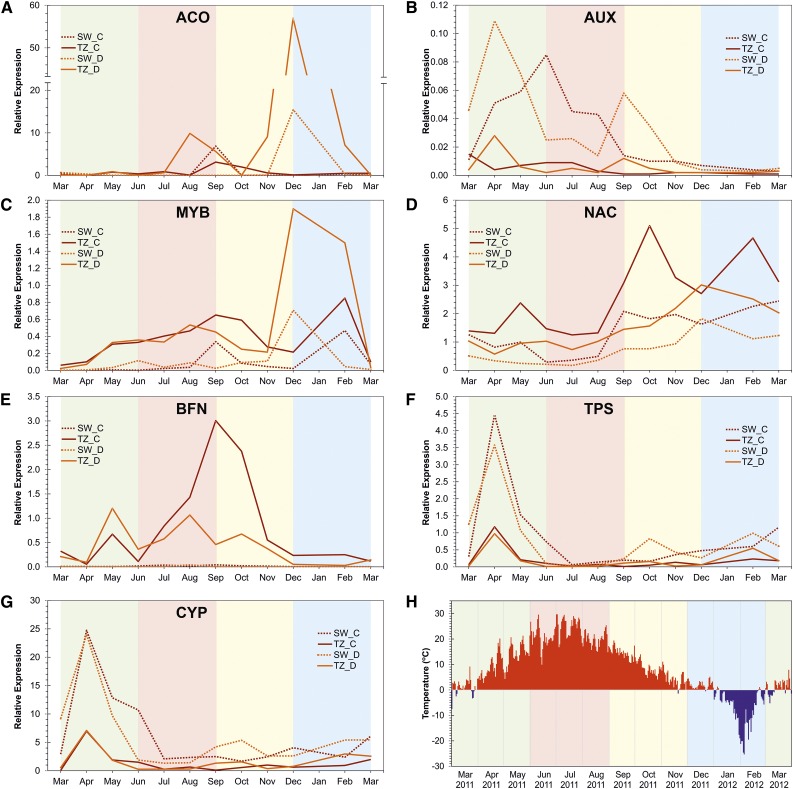
Figure 4.
Expression profile of A, ACC oxidase; B, auxin responsive protein; C, a MYB-like transcription factor; D, a NAC domain transcription factor; E, the PCD marker BFN; F, diterpene synthase; G, abietadienol/abietadienal oxidase transcripts in the TZ and SW of tree C and D; and H, the daily maximum temperature in Punkaharju where sampling took place from March 2011 to March 2012. The year-round qPCR result showed that ACC oxidase very strongly reacted to as yet undefined stimuli at different times during the year. On the other hand, the expression level of the auxin responsive transcript in the TZ was generally low and ceased in the winter. Expression profile of the MYB-like and NAC domain protein-encoding transcripts was higher in TZ in both trees, increased gradually through the summer months, and further accumulated in the winter. The expression level of BFN transcript of both trees showed an increase in May in the TZ, was maintained over the summer months, and then gradually ceased in late autumn. BFN transcript was not expressed in SW at any time. The transcription level of diterpene synthase and abietadienol/abietadienal oxidase was always greater in the SW than in the TZ in both trees. Both transcripts (in SW and TZ) started to rise in mid-spring, dropped in late spring, decreased throughout the summer, and ceased in winter. The green, red, yellow, and blue backgrounds indicate the spring, summer, autumn, and winter months, respectively. The y axis is the expression relative to the geometric mean of actin and histone transcripts.