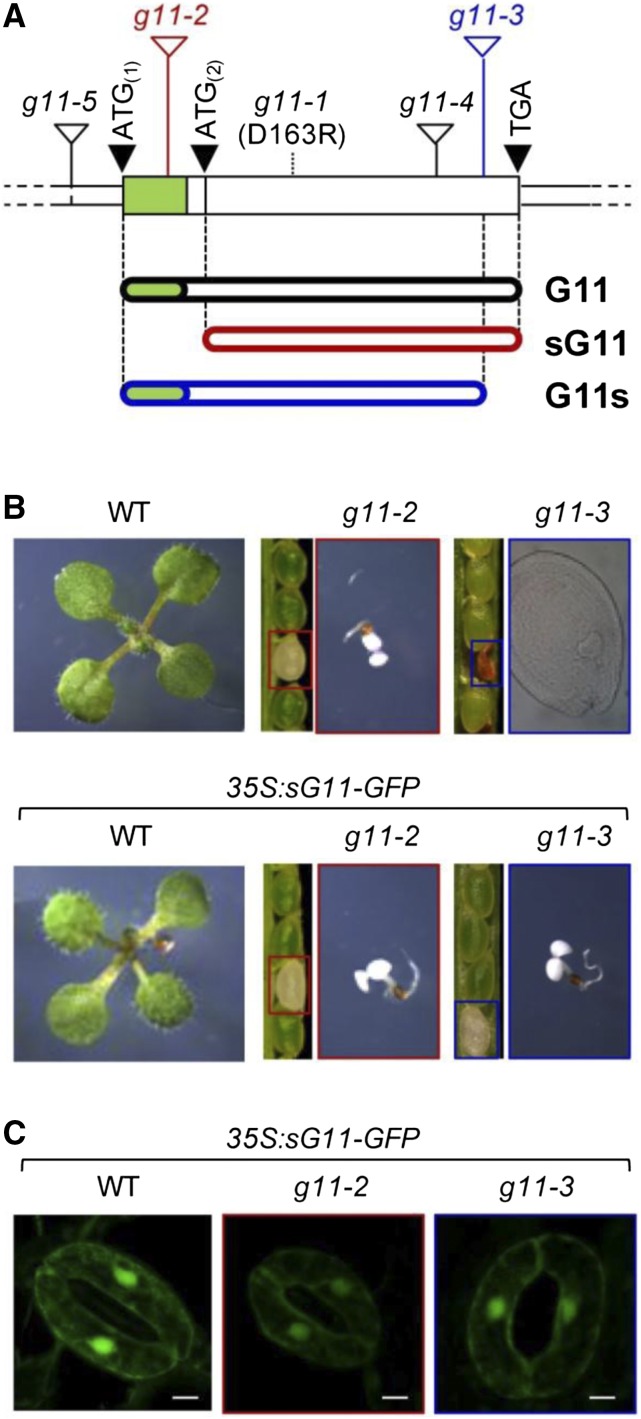
Figure 2.
G11 mutant alleles and associated phenotypes. A, G11 gene model according to TAIR v10 annotation. The protein-coding sequence (which lacks introns) is shown as a wider box with a green section corresponding to the predicted plastid targeting sequence. The position of translation start and stop codons is shown with black triangles. The position of T-DNA insertions is represented with white triangles. The position of the point mutation in the g11-1 allele is shown with a dashed line. Lower bars represent encoded proteins. B, Phenotype of G11-defective mutants either producing or not producing a sG11 protein. Representative seedlings of the indicated genotypes grown under long-day conditions for 10 d are shown to the same scale. Segregating populations of seeds in siliques of plants heterozygous for the g11-2 and g11-3 mutations is also shown. Boxed seeds correspond to the homozygous albino mutants represented in the right. Brownish seeds did not produce seedlings due to a blockage in embryo development at the heart stage (as shown in the corresponding picture). C, Cytosolic localization of the sG11-GFP protein. Pictures show GFP fluorescence from the sG11-GFP protein in stomata from 10-d-old seedlings of the indicated genotypes (bars, 5 µm).