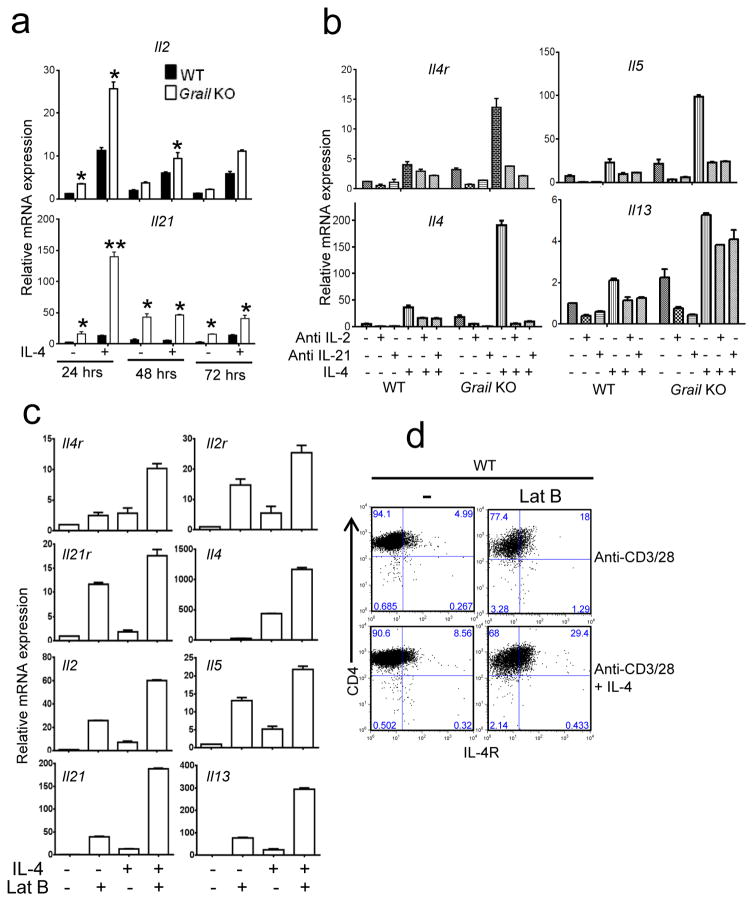
Figure 4. Grail controls IL-4 receptor expression in Th2 cells.
(a) Naïve CD4+ T cells from WT and Grail KO mice were activated with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 in the presence or absence of IL-4 for 24, 48 and 72 hours and analyzed for expression of Il2 and Il21 by qRT-PCR. (b) Naïve CD4+ T cells from WT and Grail KO mice were activated with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 along with the indicated conditions for 48 hrs and the mRNA expression of the indicated genes was analyzed. (c–d) Naïve CD4+ T cells from WT mice were activated with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 under indicated conditions and treated with an endosome inhibitor, Latrunculin B for 48 hours. (c) mRNA expression of Th2-specific genes was analyzed by qRT-PCR. (d) IL-4R protein expression was analyzed by FACS. Numbers in dot plot quadrants represent the percentages. The data shown in a, b and c were normalized by the expression of a reference gene Actb. The results shown are mean ± SEM. P values: *<0.05,**<0.01, Student’s t-test was performed to detect between-group differences.. The data are representative of at least three independent experiments with consistent results.