Figure 5.
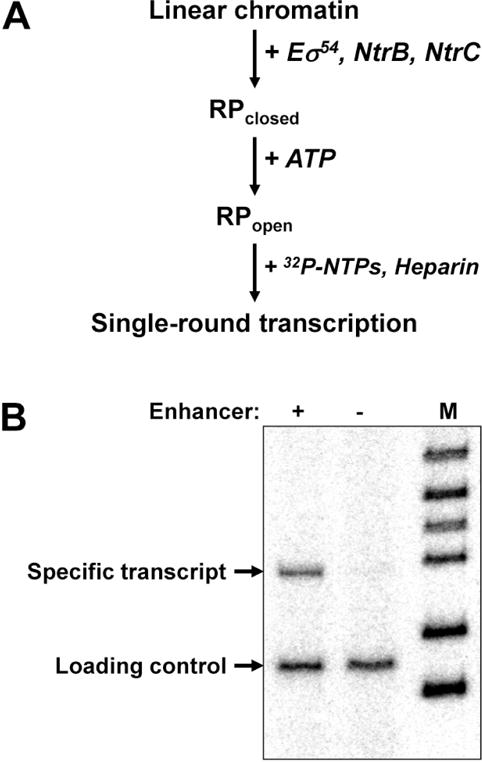
Analysis of enhancer-dependent glnAp2 promoter activation in chromatin using the single-round transcription assay. A. The experimental approach. Eσ54: RNA polymerase holoenzyme that recognizes the glnAp2 promoter. NtrB: protein kinase that phosphorylates NtrC (transcription activator that after the phosphorylation interacts with the enhancer and activates transcription). RPclosed and RPopen – closed and open initiation complexes, respectively. B. Transcription of enhancer-containing and enhancer-less saturated chromatin templates. The 3.9-kb HindIII/PstI fragment of the pYP05 plasmid containing (+) the enhancer or 3.0-kb EcoRV fragment missing it (−) were assembled into saturated arrays of nucleosomes and transcribed using the single-round transcription assay. Chromatin structure supports efficient transcription that is almost entirely enhancer-dependent. M – end-labeled pBR322-MspI digest. End-labeled DNA fragment was added to the reactions as a loading control.
