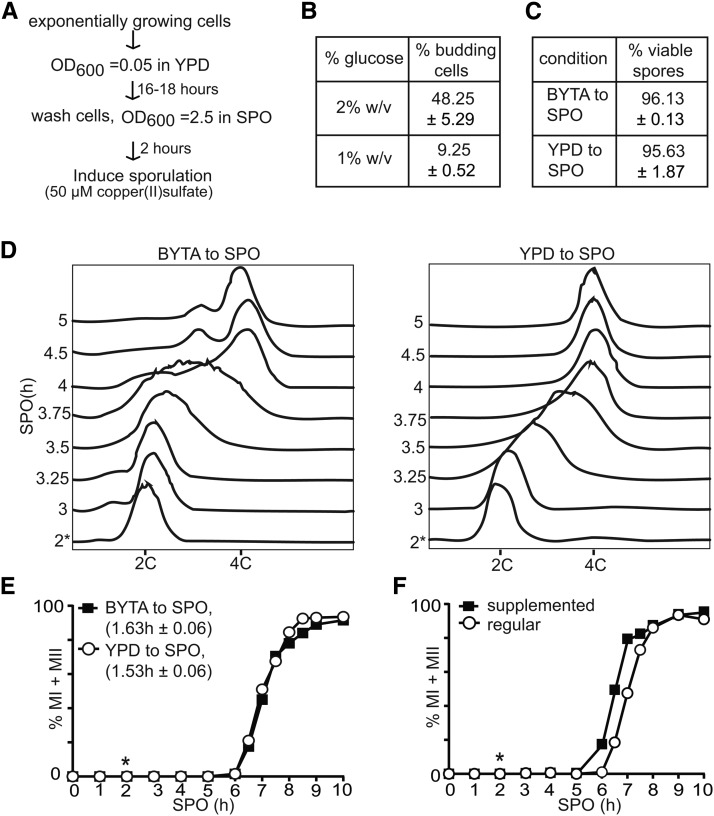
Figure 2.
Cells do not require growth in acetate-containing medium prior to induction of synchronous sporulation. (A) Flowchart for inducing synchronous sporulation. Diploid pCUP-IME1/pCUP-IME4 (FW1810) cells were grown to exponential phase for 6–7 hr in YPD. Cells were subsequently diluted to YPD medium with 1% glucose and grown for 16–18 hr to an OD600 of 11–12 to obtain mostly unbudded G1 cells. Cells were then pelleted by centrifugation, washed with sterile water and resuspended to a final OD600 of 2.5 in SPO; 50 µM copper (II) sulfate was added 2 hr after the cells were transferred to SPO to induce IME1 and IME4. (B) Budding index of cells cultured for 16 hr in YPD with different glucose concentrations. The mean and SEM from three independent experiments is shown, and n = 400 cells were counted for each repeat. (C) Spore viability of the pCUP-IME1/pCUP-IME4 strain. Cells were grown overnight in YPD, and induced to sporulate in SPO after transfer from YPD or presporulation media (BYTA). Sporulation was induced using standard protocols (BYTA to SPO), or by using the method described in (A) (YPD to SPO). Copper (II) sulfate was added 2 hr after the cells were transferred to SPO. Tetrads were collected 24 hr after IME1 induction, dissected, and assayed for viability (n = 160 spores). The mean value of three independent experiments plus the SEM is shown. (D) Flow cytometry analysis of DNA content of cells cultured in either reduced glucose YPD or presporulation medium (BYTA) before shifting to SPO. Samples were taken at indicated time points, fixed, and DNA content was measured by propidium iodide staining. At least 50,000 cells were analyzed at each time point. (E) Kinetics of meiotic divisions in cells as described in (C) and (D). For determining the kinetics of meiotic divisions, samples were taken at the indicated time point, fixed, and DAPI masses were counted. Cells that harbored two, three, or four DAPI masses were classified as cells undergoing meiosis I or meiosis II (% MI + MII). For each time point, at least 200 cells were counted. We also computed the time or period taken for 75% of the cells to complete meiotic divisions (see Materials and Methods for details). This number is displayed in brackets next to the legend, and represents the mean number of hours followed by the SEM of three independent experiments. (F) Kinetics of meiotic divisions of the pCUP-IME1/pCUP-IME4 strain as described (A) and (E), except that sporulation was induced in either regular SPO or supplemented SPO (see Materials and Methods). The graph displays a representative experiment from three repeated experiments. *, time of induction of IME1, 2 hr after the cells were transferred to SPO.