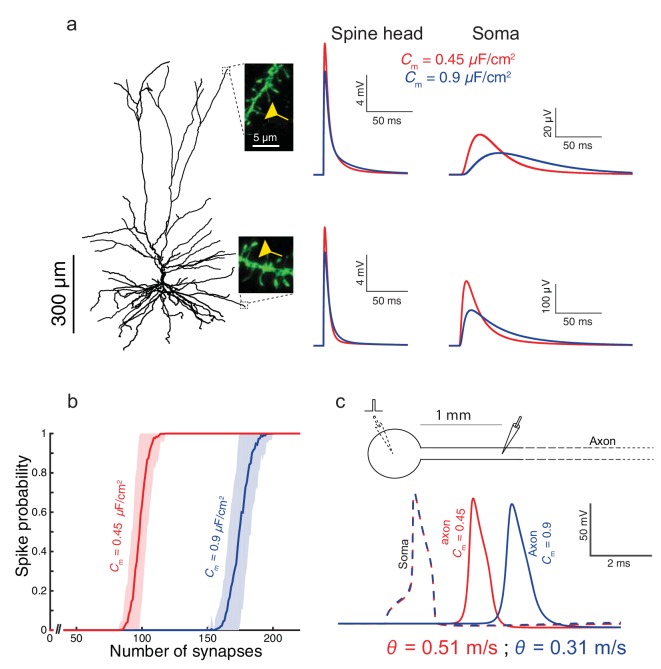
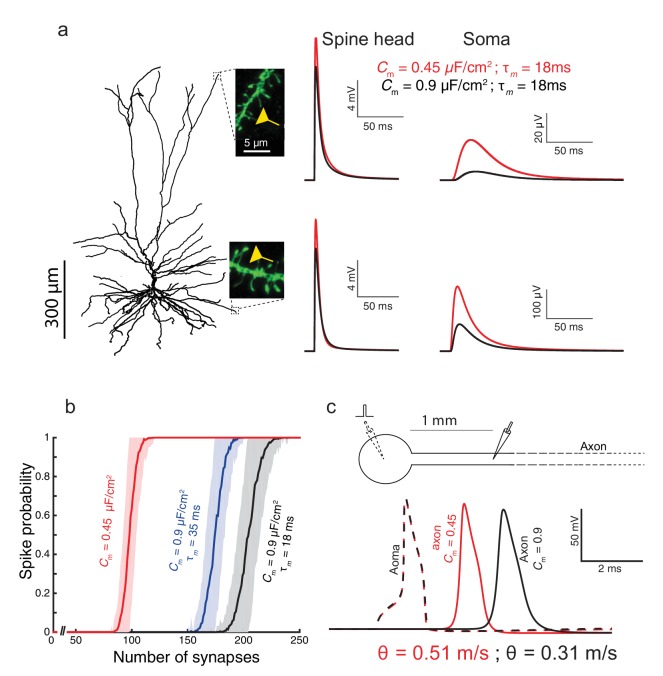
Figure 3. Functional implications of the low Cm value in human L2/3 cortical neurons for signal processing.
(a) The neuron model shown in Figure 1a, receiving an excitatory synaptic input on distal apical dendritic spine (top trace) and on a distal basal dendritic spine (lower traces). The model cell has either Cm = 0.45 μF/cm2 (red traces) or Cm = 0.9 μF/cm2 (blue traces), while the other cable parameters (Ra = 203 Ωcm, Rm = 38,907 Ωcm2) were kept fixed. Excitatory synapses were activated on the head of the modeled dendritic spine (inset, scale bar is 5 μm; see Materials and methods). Note the larger and faster somatic EPSP for the red case. (b) For the cell model shown in a, significantly smaller number of excitatory spinous synapses were required for initiation of a somatic spike when Cm = 0.45 μF/cm2. Synapses were simultaneously activated and distributed randomly over the dendritic tree (see Materials and methods). (c) Top, schematics of soma and axon of the cell modeled in a., the axon had a diameter of 1 µm. Bottom, the velocity (θ) of the axonal spike, measured at 1 mm from the soma, is significantly increased (by about 65%) with Cm = 0.45 μF/cm2 (red spike); the amplitude of the propagated axonal spike is also slightly increased in this case.