Fig. 8.
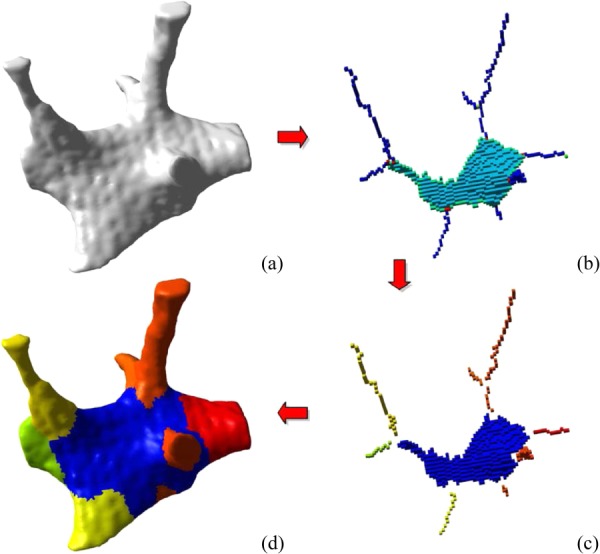
Spatial decomposition of trabecular bone. The initial binary image that served as input for our algorithm is shown in panel (a). A skeletonization and optimization algorithm is applied to get a homotopic shape preserving skeleton as shown in panel (b). This skeleton is then point-classified, thus arc-, surface-, border-, and intersection-points are shown in different colors. (c) This point-classified skeleton is then spatially decomposed by removing the intersection points. (d) A two-way multicolor dilation algorithm was applied to find the volumetric extend of each element, yielding in the final spatially decomposed structure. (From Reference 7 with permission.)
