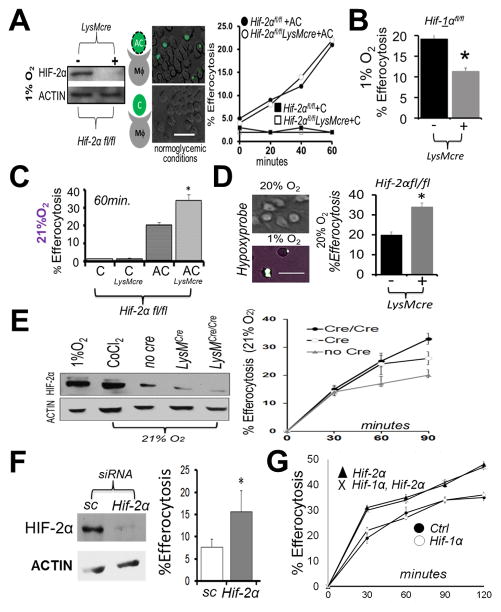
Figure 1. Hif-2α is not required for hypoxic efferocytosis, in contrast to under non-hypoxic conditions, where Hif-2α specifically acts as an efferocytic suppressor.
(A) Immunoblot of Hif-2αfl/fl LysMcre bone marrow-derived macrophages (Mϕs) after culture at 1% oxygen. Mϕs were overlaid with fluorescent (calcein-AM) apoptotic Jurkat T-cells (“AC”) or fluorescent viable Jurkat T-cells (“C”) and efferocytosis quantified. Scale bar = 60 micrometers. (B) Efferocytosis carried out similar to as in (A) except during with Hif-1αfl/fl vs. Hif-1αfl/fl LysMcre Mϕs. (C) Efferocytosis similar to as in (A) except under normoxia. (D) Efferocytosis by Hif-2αfl/fl vs Hif-2αfl/fl LysMcre phagocytes cultured on gas permeable plates. Wild type cultures were grown on Lumox plates to optimize gas exchange at indicated oxygen tensions and stained with hypoxyprobe (green) as an indicator of hypoxia. Efferocytosis of fluorescent apoptotic Jurkat cells by Hif-2αfl/fl vs. Hif-2αfl/fl LysMcre phagocytes after quantification by microscopy. (E) Immunoblots of HIF-2α levels as a function of efferocytosis efficiency. (F) Immunoblot of normoxic Mϕ HIF-2α after Hif-2α siRNA in mature Mϕs and % Efferocytosis at 30min. Sc = scrambled siRNA. (G) Normoxic efferocytosis kinetics of Hif-2αfl/fl LysMcre vs. Hif-1αfl/fl Hif-2αfl/fl LysMcre vs. Hif-1αfl/fl LysMcre vs. control (Hif- 1αfl/fl Hif-2αfl/fl). * indicates < 0.05 relative to control.