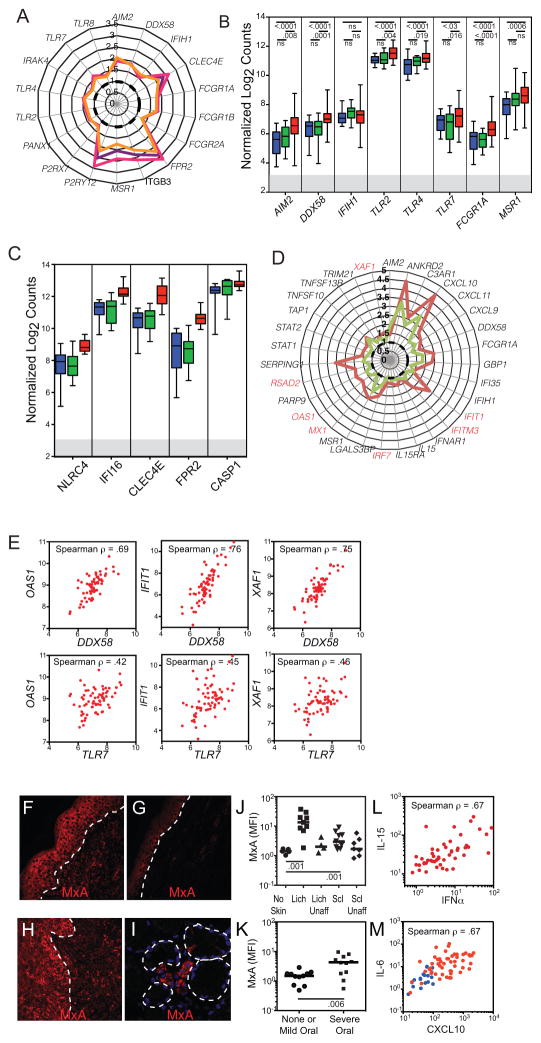
Figure 3.
Monocyte expression of innate immune receptors for DAMP and of Type I IFN induced genes. A. Polar plot of median fold change in microarray-assessed gene expression (as compared to the median in normal controls (dotted black line)) of innate immune receptors for DAMP in all CGVHD patients (purple line), in patients with either severe oral CGVHD or moderate to severe lichenoid cutaneous CGVHD (fuschia line) or in patients with widespread (>30% body surface area) deep and dermal sclerosis (orange line). B–C. Box and whisker plot comparing Nanostring-analyzed expression of several DAMP responsive genes in monocytes sorted from 19 normal controls (blue), 14 nonCGVHD (green) and 69 CGVHD patients (red). C. Box and whisker plots from a 12 severe CGVHD patients from the main cohort, retested with additional DAMP receptors. D. Polar plot of median fold change in gene expression of IFN-inducible genes in CGVHD microarray patients whose IRF7 expression was greater than the median (brown line) versus those with less than the median (green line). Type I IFN-specific genes marked in red. E. Scatter plots of Nanostring-assessed expression of OAS1, IFIT1, and XAF1 as compared with DDX58 and TLR7, demonstrating correlated expression of DAMP receptors and Type I IFN-inducible genes in CGVHD monocytes (red). (F–I) Fluorescence immunohistochemistry of the Type I-IFN induced protein MxA, showing expression in biopsies collected from affected (F) lichenoid skin, (G) sclerotic skin, (H) oral mucosa and (I) minor salivary gland. Tissues were formalin fixed, paraffin embedded, and following antigen retrieval and staining with MxA and AlexaFluor 555 secondary antibodies, were imaged on a Leica SP2 confocal microscope. Dotted lines mark the interface between epidermis and dermis or outline secretory acini. J–K. Immunofluorescent expression (mean fluorescent intensity) of MxA in epidermal keratinocytes in CGVHD tissues. J. Comparison of biopsies of skin from CGVHD patients with no skin involvement, with lichenoid (lich) involvement, or sclerotic (scl) involvement. Paired biopsies of affected and unaffected skin were collected from each lichenoid or sclerotic patient. K. Comparison of biopsies of oral mucosa from patients with no oral CGVHD or only mild symptoms, versus those with severe oral CGVHD. L. Scatter plots showing correlated increases in IFNα and IL-15 in 49 CGVHD natural history patients, of which 24 had more than 20% of body surface area affected with Lich-CGVHD or Scl-CGVH. M. Scatter plots showing correlated increases in IFNα inducible CXCL10 and IL-6 in 49 CGVHD natural history patients, including 23 of the microarray patients, and 12 normal controls. This assay was repeated 3 times with plasma from different cohorts of 40–50 CGVHD patients.