Figure 2. IRF7 is a direct transcriptional target of MYC in pDC.
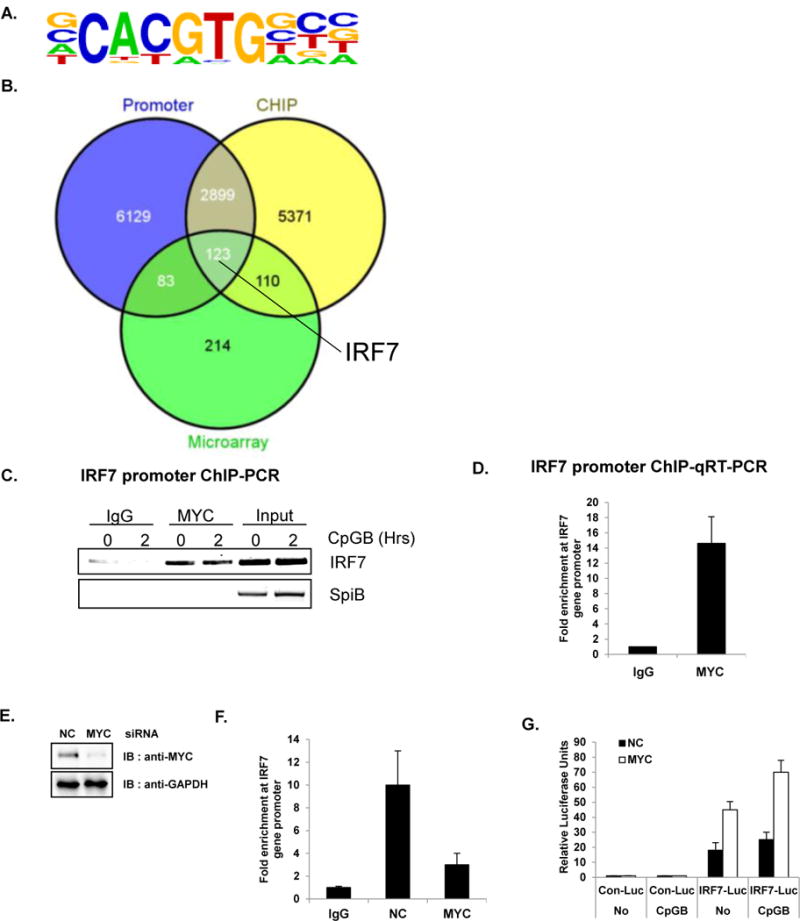
Direct target genes of MYC were identified using ChIP-Seq. (A–D) GEN2.2 (unstimulated or CpGB-treated) cells were cross-linked and immunoprecipitated with anti-MYC antibody or rabbit IgG control. In parallel, cross-linked input (without antibody) was put aside for the comparison. The bound DNAs were sequenced using HiSeq 2000 (Illumina) (A) The most highly enriched motif (46.2% of Targets, with p-value 1 e-847) were analyzed and presented using Homer de novo motif analysis (B) The Venn diagram shows the intersections of ChIP-Seq, promoter analysis, and microarray. Putative direct target genes of MYC (123 genes listed in Table S2) include IRF7. Venn diagrams were constructed using Venny. (C) The immunoprecipitated chromatin was isolated and used for semiquantitative RT-PCR with IRF7 promoter primers. MYC directly binds to the promoter region of IRF7. SpiB, another important transcription factor for pDC development was used as a negative control. Data are representative of three independent experiments. (D) Amplification of the IRF7 promoter was visualized using qRT-PCR by comparing to input sample signals (1% of total crude). The levels of IRF7 promoter in MYC-bound or control IgG-bound DNA were normalized to input and expressed as fold difference between the two samples. Data are representative of three independent experiments (average of triplicates ± standard deviation) (E) GEN2.2 cells were nucleofected with siRNA against NC or MYC and then analyzed for knockdown efficiency by western blot analysis. (F) GEN2.2 cells nucleofected with siRNA against NC or MYC were cross-linked and immunoprecipitated with anti-MYC antibody or rabbit IgG control. Amplification of the IRF7 promoter was visualized using qRT-PCR by comparing to input sample signals (1% of total crude). The levels of IRF7 promoter in MYC-bound or control IgG-bound DNA were normalized to input and expressed as fold difference between the two samples. Data are representative of three independent experiments (average of triplicates ± standard deviation) (G) Depletion of MYC showed an enhanced basal promoter activity of IRF7. HEK 293T cells stably expressing TLR9 were transiently co-transfected with luciferase reporter plasmid conjugated with control or human IRF7 promoter and transfected with MYC or NC siRNA. Twenty-four hours after transfection, cells were further stimulated with or without CpGB. Dual luciferase assays were performed 8 h after CpGB stimulation. All luciferase activity was normalized to the expression of the Renilla luciferase activity. The results were visualized as a fold of induction over the unstimulated- NC siRNA transfected GEN2.2 cells. Data are representative of three independent experiments (average of triplicates ± standard deviation)
