Fig. 2.
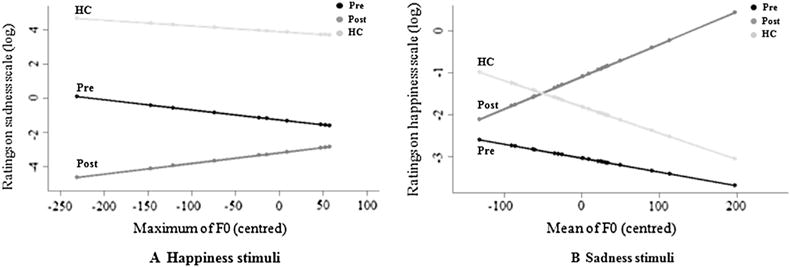
Differential impact of acoustic features on vocal emotion recognition between the preoperative, post-operative, and HC groups, after controlling for participant effect, excess zero pattern, and main effects of group and acoustic feature, as well as the effects of the remaining Group × Acoustic feature interactions. (A) Differential impact of maximum fundamental frequency (F0), perceived as pitch, on the Sadness scale when the stimulus was “happiness” between the preoperative (black), post-operative (dark grey), and HC (in light grey) groups. (B) Differential impact of mean F0 on the Happiness scale when the stimulus was “sadness” between the preoperative (black), post-operative (dark grey), and HC (light grey) groups.
