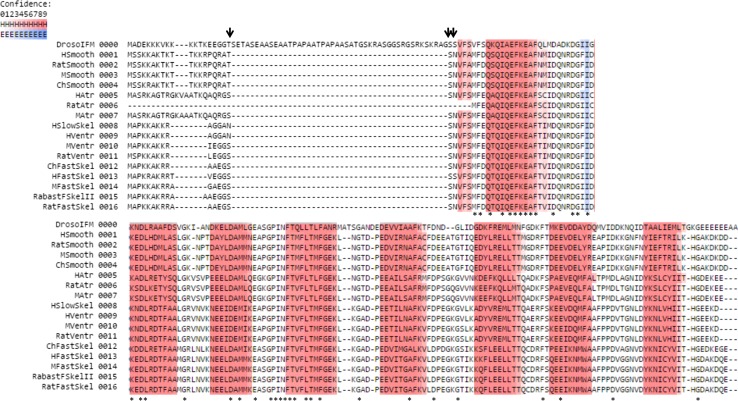
Fig. 2.
Multiple sequence alignment (MSA) of different RLC isoforms from different laboratory model organisms and humans showing eight conserved predicted helices (red) forming part of the conserved four EF-hand secondary structure. The helix-loop prediction was performed in the Ali2D Bioinformatics toolkit of the Max Plank Institute of Developmental Biology (http://toolkit.tuebingen.mpg.de/ali2d). The degree of confidence in prediction secondary structure is color coded in shades of increasing color intensity indicating increasing prediction confidence (for helix (H): white to dark red, for loops (E): white to dark blue). The black arrows indicate the conserved sites of physiologically relevant phosphorylation sites of RLC across species and tissues. The asterisks (*) indicate conserved residues across the sequences in the MSA. Sequences were retrieved from NCBI. Abbreviations used for biological sources of RLC sequences with their respective gene names and NCBI protein accession numbers are as follows: DrosoIFM (Drosophila indirect flight muscle, MLC2, P18432.2), HSmooth (human smooth muscle, MYL12B, O14950.2), RatSmooth (rat smooth muscle, MYL12B, P18666.3), MSmooth (Mouse smooth muscle, MYL12B, Q3THE2.2), ChSmooth (chicken smooth muscle, MYL12A, P24032.2), HAtr (human atrial muscle, MYL7, Q01449.1), RatAtr (rat atrial muscle, MYL7, NP_001099487.1), MAtr (mouse atrial muscle, MYL7, Q9QVP4.1), HSlowSkel (human slow skeletal muscle, same as human ventricular), HVentr (human ventricular muscle, MYL2, P10916.3), MVentr (mouse ventricular muscle, MYL2, P51667.3), RatVentr (rat ventricular muscle, MYL2, P08733.2), ChFastSkel (chicken fast skeletal muscle, MYLPF, P02609.2), HFastSkel (human fast skeletal muscle, MYLPF, Q96A32.1), MFastSkel (mouse fast skeletal muscle, MYLPF, P97457.3) RabastFSkelII (rabbit fast skeletal type II muscle, MYLPF, P02608.3), RatFastSkel (rat fast skeletal muscle, MYLPF, P04466.2)