FIG 5 .
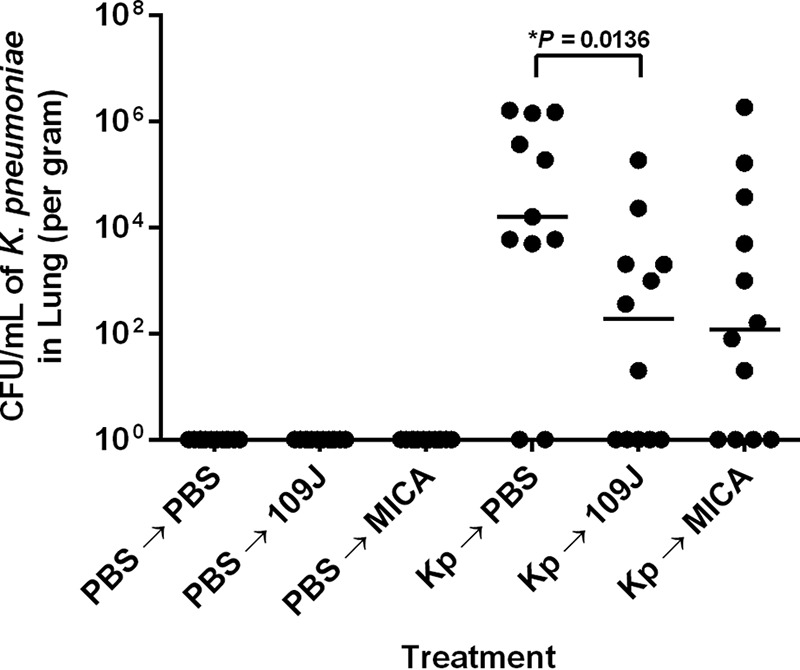
K. pneumoniae bacterial burden within lungs of rats after treatment with predatory bacteria. K. pneumoniae (or PBS for control groups) was initially introduced into the lungs of rats via intranasal inoculation. Animals were then treated with PBS, B. bacteriovorus 109J, or M. aeruginosavorus (MICA) at 30 min and 6, 12, and 18 h postinoculation. At 24 h, lungs were harvested, homogenized, and plated on MacConkey agar plates to recover K. pneumoniae CFU. Twelve rats per treatment group were used at each time point. Each data point represents a single rat’s respective bacterial load. Horizontal lines represent the median of the results from each treatment set. Data are combined from the results from two independent experiments. Analyses of significant differences between treatment groups and respective controls were performed using the Mann-Whitney test (*, P < 0.05).
