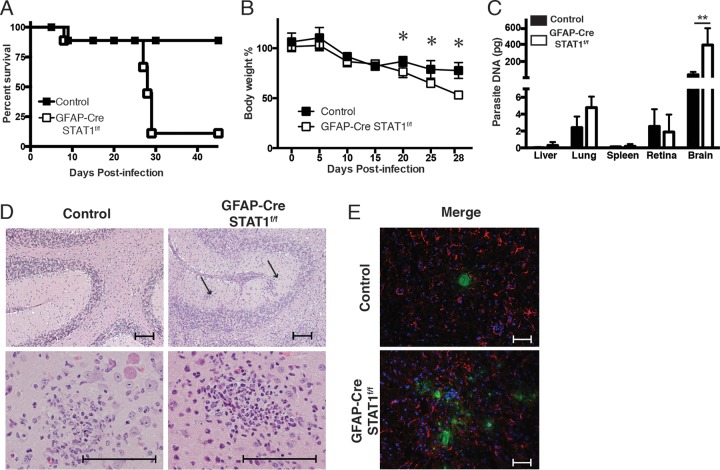
FIG 3 .
Increased susceptibility of GFAP-Cre STAT1f/f mice to toxoplasmic encephalitis. (A and B) Control and GFAP-Cre STAT1f/f mice were infected i.p. with 20 cysts of the ME49 strain of T. gondii, and survival (represented by Kaplan-Meier analysis) (A) and weight loss (B) were assessed. Data for five mice per group and a combination of two independent experiments are shown. (C) Real-time PCR specific for the Toxoplasma B1 repeat region was used to quantify the amount of parasite DNA from 500 ng of DNA purified from lung, liver, spleen, retina, and brain at 25 dpi. These graphs are means ± standard errors of the means and show the pooled averages from three independent experiments. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01. (D) Representative hematoxylin-and-eosin-stained sections of the brains of control and GFAP-Cre STAT1f/f mice infected for 25 days. Bar, 100 µm. (E) Frozen tissue sections from the brains of infected control and GFAP-Cre STAT1f/f mice were used for IHC detection of T. gondii (green) or GFAP (red), with DAPI (blue) as a nuclear counterstain. Bar, 50 µm.