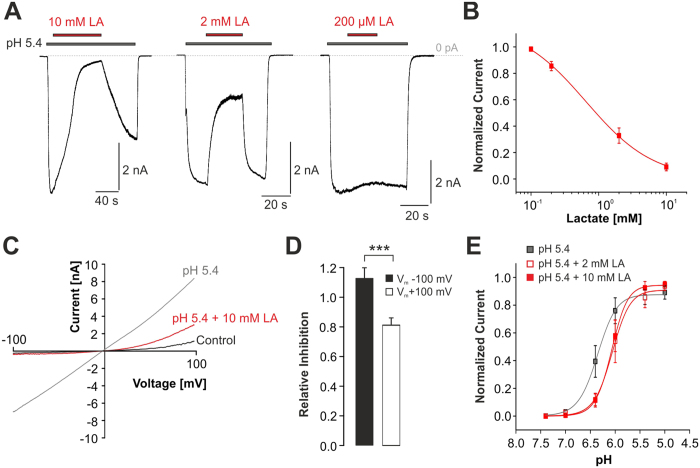
Figure 1. Inhibition of proton-evoked TRPV1 currents by LA.
(A) Representative recordings demonstrating inhibition of a pH 5.4-induced inward current by LA at different concentrations. Cells were held at −60 mV and the co-application of LA and pH 5.4 was started once the pH 5.4-induced inward current had reached a steady-state. (B) Concentration-dependency of LA-induced inhibition of proton-evoked inward currents. Current amplitudes were normalized to those before LA application. The solid line represents a fit with the Hill equation. (C) Membrane currents of TRPV1 monitored during 500-ms long voltage ramps from −100 mV to +100 mV in presence of control solution, pH 5.4 or pH 5.4 + 10 mM LA. (D) Mean relative inhibition of pH 5.4-induced inward currents at −100 mV and outward currents at +100 mV by 10 mM LA. The average relative inhibition = 1 − I/I0 for each concentration was determined by normalization; where I = current in presence of LA, I0 = current in absence of LA. Inward currents were significantly stronger inhibited as compared to outward currents. (E) Concentration-dependent activation of TRPV1 by protons applied alone or in combination with 2 or 10 mM LA. Peak current amplitudes were normalized to the largest current amplitude in the respective cells and plotted against the corresponding pH-values. The solid lines represent fits with the Hill equation. Data are presented as mean ± S.E.M. Statistical differences are indicated by ***p < 0.001.