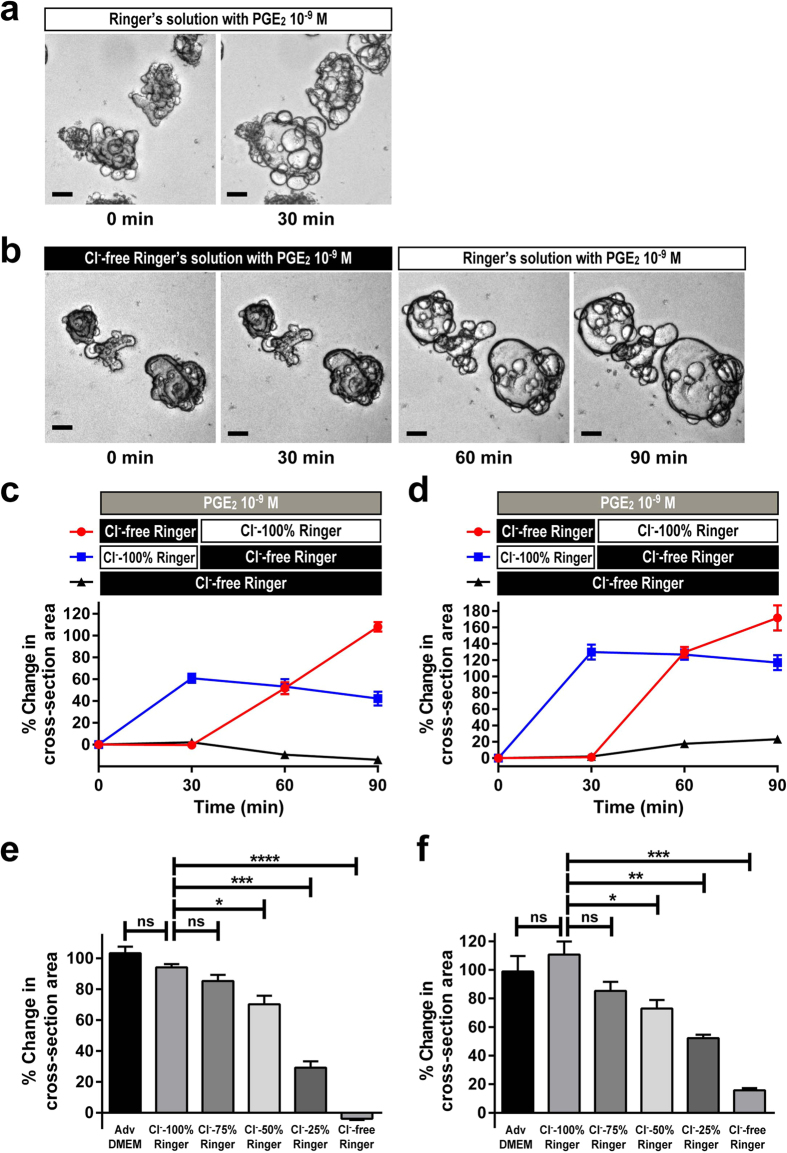
Figure 4. PGE2-induced organoid swelling is dependent on Cl−.
The PGE2-induced swelling of jejunal organoids was tested under normal, Cl− reduced and Cl− depleted buffer conditions. (a) Phase contrast view of the PGE2-induced swelling in Ringer’s solution supplemented with standard Cl− level (126.8 mEq). PGE2 (10−9 M) was added to jejunal organoids for 30 min at 7 days after passage. Note that the swelling response is completely maintained. Scale bar represents 100 μm. (b) Phase contrast view of the PGE2-induced swelling in Cl−-free Ringer’s solution. PGE2 (10−9 M) was added to jejunal organoids for 30 min at 7 days after passage. Note that the swelling response is completely abolished by Cl− depletion, but can be restored by the following addition of buffer supplemented with Cl− (126.8 mEq). Scale bar represents 100 μm. (c,d) Time course experiment lasting up to 90 min showing the swelling response to PGE2 under normal or Cl−-free Ringer’s solution. Jejunal organoids established from the uninflamed region of a CD patient (c) and those established from the healthy mucosa of a non-IBD patient (d) were subjected to the PGE2-induced swelling (10−9 M) under normal or Cl−-free Ringer’s solution, and the response was quantified by the 3D-scanning system. (e,f) Quantification of the PGE2-induced swelling under different Cl− concentrations. Jejunal organoids established from the uninflamed region of a CD patient (e) and those established from the healthy mucosa of a non-IBD patient (f) were subjected to the PGE2-induced swelling (10−9 M) under different Cl− concentrations, and the response was quantified by the 3D-scanning system. Data are shown as the mean ± SEM of three independent wells. *indicates P < 0.05, ***indicates P < 0.0005, ****indicates P < 0.0001 as determined by two-sided Student’s t-test compared to the data of control (Adv DMEM; Advanced DMEM) or Cl− 100% Ringer. ns indicates not significant. All results are representative of at least three independent experiments.