Fig. 10.
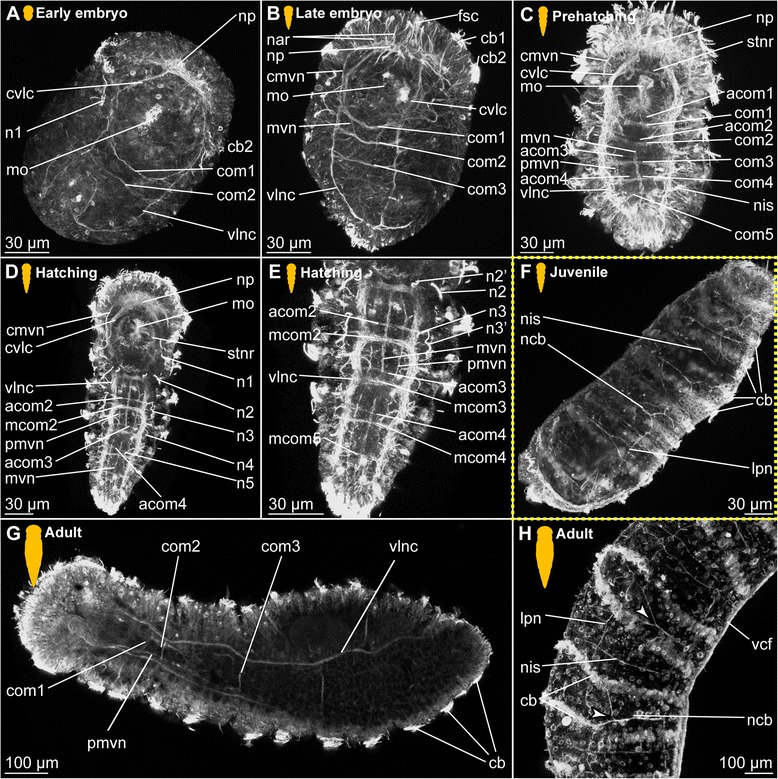
Development of the nervous system in Dinophilus taeniatus. Acetylated α-tubulin-like immunoreactive filaments shown in white, animals are oriented with the anterior end up (a-f, h) or to the left (g). Stages are indicated by silhouettes next to the figure capture, and the assignment to the respective stage next to them. The first signs of difference between the two species D. gyrociliatus and D. taeniatus are emphasized by a yellow dashed-lined frame around the picture. a-c embryonic development: a ventral view of an early embryo, note a dumbbell like shape of the neuropil, b ventral view of a late embryo, c ventral view of a prehatching embryo, d ventral view of the central nervous system in an early juvenile, e detail of the posterior part of the nervous system in an early juvenile, note the peculiar sets of acetylated α-tubulin-like immunoreactive structures forming the protonephridia, f left lateral view of a juvenile specimen with details of the peripheral nerves, g, h adult: g ventral view of the major parts of the ventral nervous system, h lateral view of the trunk of an adult specimen with details of peripheral nerves, note bifurcations (indicated by arrowheads) of ciliary band nerves. Abbreviations: acom – anterior commissure, cb – ciliary band, cmvn – circumesophageal commissure forming the medioventral nerve, com1-5 – commissure 1–5, cvlc – circumesophageal commissure forming the ventrolateral nerve cord, fsc – flask-shaped cells, lpn – longitudinal peripheral nerve, mcom – median commissure, mo – mouth opening, mvn – medioventral nerve, n1-5 – nephridium 1–5, n2′, n3′ additional part of respective nephridium, nar – nerves innervating the anterior rim, ncb – nerve of the ciliary band, nis – intersegmental lateral nerve, np – neuropil, pmvn – paramedioventral nerve, stnr – stomatogastric nerve ring, vcf – ventral ciliary field, vlnc – ventrolateral nerve cord
